Signaling by STATs
- PMID: 15225360
- PMCID: PMC464899
- DOI: 10.1186/ar1197
Signaling by STATs
Abstract
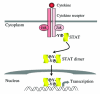
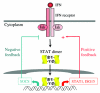
A variety of cytokines and growth factors use the Janus kinase (Jak)-STAT signaling pathway to transmit extracellular signals to the nucleus. STATs (signal transducers and activators of transcription) are latent cytoplasmic transcription factors. There are seven mammalian STATs and they have critical, nonredundant roles in mediating cellular transcriptional responses to cytokines. The physiological roles of STATs have been elucidated by analysis of mice rendered deficient in STAT genes. STAT activation is regulated and can be modulated in a positive or negative fashion; it can be reprogrammed to drive different cellular responses. Several auto-regulatory and signaling crosstalk mechanisms for regulating Jak-STAT signaling have been described. Understanding and manipulation of the function of STATs will help in the development of therapeutic strategies for diseases that are regulated by cytokines.
Figures
References
-
- Darnell JE, Jr, Kerr IM, Stark GR. Jak–STAT pathways and transcriptional activation in response to IFNs and other extracellular signaling proteins. Science. 1994;264:1415–1421. - PubMed
-
- Gauzzi MC, Barbieri G, Richter MF, Uze G, Ling L, Fellous M, Pellegrini S. The amino-terminal region of Tyk2 sustains the level of interferon alpha receptor 1, a component of the interferon alpha/beta receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1997;94:11839–11844. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.22.11839. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mowen KA, Tang J, Zhu W, Schurter BT, Shuai K, Herschman HR, David M. Arginine methylation of STAT1 modulates IFNalpha/beta-induced transcription. Cell. 2001;104:731–741. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

