Degradation of promoter-bound p65/RelA is essential for the prompt termination of the nuclear factor kappaB response
- PMID: 15226358
- PMCID: PMC2213320
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20040196
Degradation of promoter-bound p65/RelA is essential for the prompt termination of the nuclear factor kappaB response
Abstract
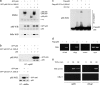
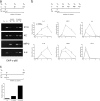
Transcription factors of the nuclear factor (NF)-kappaB/Rel family translocate into the nucleus upon degradation of the IkappaBs. Postinduction repression of NF-kappaB activity depends on NF-kappaB-regulated resynthesis of IkappaBalpha, which dissociates NF-kappaB from DNA and exports it to the cytosol. We found that after activation, p65/RelA is degraded by the proteasome in the nucleus and in a DNA binding-dependent manner. If proteasome activity is blocked, NF-kappaB is not promptly removed from some target genes in spite of IkappaBalpha resynthesis and sustained transcription occurs. These results indicate that proteasomal degradation of p65/RelA does not merely regulate its stability and abundance, but also actively promotes transcriptional termination.
Figures


References
-
- Siebenlist, U., G. Franzoso, and K. Brown. 1994. Structure, regulation and function of NF-kappa B. Annu. Rev. Cell Biol. 10:405–455. - PubMed
-
- Verma, I.M., J.K. Stevenson, E.M. Schwarz, D. Van Antwerp, and S. Miyamoto. 1995. Rel/NF-kappa B/I kappa B family: intimate tales of association and dissociation. Genes Dev. 9:2723–2735. - PubMed
-
- Baldwin, A.S., Jr. 1996. The NF-kappa B and I kappa B proteins: new discoveries and insights. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 14:649–683. - PubMed
-
- Whiteside, S.T., and A. Israel. 1997. I kappa B proteins: structure, function and regulation. Semin. Cancer Biol. 8:75–82. - PubMed
-
- Karin, M., and Y. Ben-Neriah. 2000. Phosphorylation meets ubiquitination: the control of NF-[kappa]B activity. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 18:621–663. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

