One recognition sequence, seven restriction enzymes, five reaction mechanisms
- PMID: 15226412
- PMCID: PMC443551
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkh685
One recognition sequence, seven restriction enzymes, five reaction mechanisms
Abstract
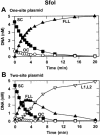
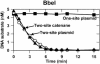
The diversity of reaction mechanisms employed by Type II restriction enzymes was investigated by analysing the reactions of seven endonucleases at the same DNA sequence. NarI, KasI, Mly113I, SfoI, EgeI, EheI and BbeI cleave DNA at several different positions in the sequence 5'-GGCGCC-3'. Their reactions on plasmids with one or two copies of this sequence revealed five distinct mechanisms. These differ in terms of the number of sites the enzyme binds, and the number of phosphodiester bonds cleaved per turnover. NarI binds two sites, but cleaves only one bond per DNA-binding event. KasI also cuts only one bond per turnover but acts at individual sites, preferring intact to nicked sites. Mly113I cuts both strands of its recognition sites, but shows full activity only when bound to two sites, which are then cleaved concertedly. SfoI, EgeI and EheI cut both strands at individual sites, in the manner historically considered as normal for Type II enzymes. Finally, BbeI displays an absolute requirement for two sites in close physical proximity, which are cleaved concertedly. The range of reaction mechanisms for restriction enzymes is thus larger than commonly imagined, as is the number of enzymes needing two recognition sites.
Figures





Similar articles
-
The type IIs restriction endonuclease BspMI is a tetramer that acts concertedly at two copies of an asymmetric DNA sequence.J Biol Chem. 2002 Feb 8;277(6):4034-41. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M108442200. Epub 2001 Nov 29. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 11729188
-
Simultaneous binding of three recognition sites is necessary for a concerted plasmid DNA cleavage by EcoRII restriction endonuclease.J Mol Biol. 2006 Apr 28;358(2):406-19. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2006.02.024. Epub 2006 Feb 28. J Mol Biol. 2006. PMID: 16529772
-
Reactions of type II restriction endonucleases with 8-base pair recognition sites.J Biol Chem. 1999 Dec 17;274(51):36379-86. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.51.36379. J Biol Chem. 1999. PMID: 10593932
-
[Type IIE and IIF restriction endonucleases interacting with two recognition sites in DNA].Mol Biol (Mosk). 2004 Sep-Oct;38(5):886-900. Mol Biol (Mosk). 2004. PMID: 15554190 Review. Russian.
-
The type IIB restriction endonucleases.Biochem Soc Trans. 2010 Apr;38(2):410-6. doi: 10.1042/BST0380410. Biochem Soc Trans. 2010. PMID: 20298193 Review.
Cited by
-
A switch in the mechanism of communication between the two DNA-binding sites in the SfiI restriction endonuclease.J Mol Biol. 2007 Nov 9;373(5):1169-83. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2007.08.030. Epub 2007 Aug 21. J Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17870087 Free PMC article.
-
Illuminating the reaction pathway of the FokI restriction endonuclease by fluorescence resonance energy transfer.Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Feb;40(3):1203-13. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr809. Epub 2011 Oct 12. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 21993298 Free PMC article.
-
Type II restriction endonucleases--a historical perspective and more.Nucleic Acids Res. 2014 Jul;42(12):7489-527. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku447. Epub 2014 May 30. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014. PMID: 24878924 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Translocation, switching and gating: potential roles for ATP in long-range communication on DNA by Type III restriction endonucleases.Biochem Soc Trans. 2011 Apr;39(2):589-94. doi: 10.1042/BST0390589. Biochem Soc Trans. 2011. PMID: 21428945 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The single polypeptide restriction-modification enzyme LlaGI is a self-contained molecular motor that translocates DNA loops.Nucleic Acids Res. 2009 Nov;37(21):7219-30. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkp794. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009. PMID: 19783815 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Roberts R.J. and Halford,S.E. (1993) Type II restriction endonucleases. In Linn,S.M., Lloyd,R.S. and Roberts,R.J. (eds), Nucleases. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY, pp. 35–88.
-
- Halford S.E. (2001) Hopping, jumping and looping by restriction enzymes. Biochem. Soc. Trans., 29, 363–374. - PubMed
-
- Roberts R.J., Belfort,M., Bestor,T., Bhagwat,A.S, Bickle,T.A., Bitinaite,J., Blumenthal,R.M., Degtyarev,S.K., Dryden,D.T.F., Dybvig,K. et al. (2003) A nomenclature for restriction enzymes, DNA methyltransferases, homing endonucleases and their genes. Nucleic Acids Res., 31, 1805–1812. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

