U1A inhibits cleavage at the immunoglobulin M heavy-chain secretory poly(A) site by binding between the two downstream GU-rich regions
- PMID: 15226420
- PMCID: PMC434241
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.24.14.6162-6171.2004
U1A inhibits cleavage at the immunoglobulin M heavy-chain secretory poly(A) site by binding between the two downstream GU-rich regions
Abstract
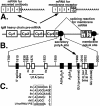
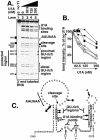
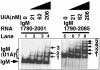
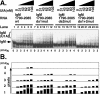
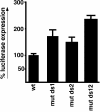
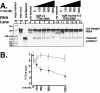
The immunoglobulin M heavy-chain locus contains two poly(A) sites which are alternatively expressed during B-cell differentiation. Despite its promoter proximal location, the secretory poly(A) site is not expressed in undifferentiated cells. Crucial to the activation of the secretory poly(A) site during B-cell differentiation are changes in the binding of cleavage stimulatory factor 64K to GU-rich elements downstream of the poly(A) site. What regulates this change is not understood. The secretory poly(A) site contains two downstream GU-rich regions separated by a 29-nucleotide sequence. Both GU-rich regions are necessary for binding of the specific cleavage-polyadenylation complex. We demonstrate here that U1A binds two (AUGCN(1-3)C) motifs within the 29-nucleotide sequence and inhibits the binding of cleavage stimulatory factor 64K and cleavage at the secretory poly(A) site.
Figures

References
-
- Berberich, I., and A. Schimpl. 1990. Regulation of Ig gene expression in normal lymphocytes. I. The half-life of secreted mu chain mRNA differs from that of membrane mu chain mRNA in resting and activated B cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 20:445-448. - PubMed
-
- Boelens, W. C., E. J. R. Jansen, W. J. van Venrooij, R. Stripecke, I. W. Mattaj, and S. I. Gunderson. 1993. The human U1 snRNP-specific U1A protein inhibits polyadenylation of its own pre-mRNA. Cell 72:881-892. - PubMed
-
- Early, P., J. Rogers, M. Davis, K. Calame, M. Bond, R. Wall, and L. Hood. 1980. Two mRNAs can be produced from a single immunoglobulin μ gene by alternative RNA processing pathways. Cell 20:313-319. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
