Effective use of TNF antagonists
- PMID: 15228618
- PMCID: PMC2833462
- DOI: 10.1186/ar997
Effective use of TNF antagonists
Abstract
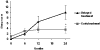
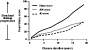
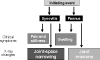
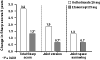
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) antagonists are biologic response modifiers that have significantly improved functional outcomes in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). RA is a progressive disease in which structural joint damage can continue to develop even in the face of symptomatic relief. Before the introduction of biologic agents, the management of RA involved the use of disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) early in the course of disease. This focus on early treatment, combined with the availability of the anti-TNF agents, has contributed to a shift in treatment paradigms favoring the early and timely use of DMARDs with biologic therapies. Improvement in symptom control does not always equate to a reduction in disease progression or disability. With the emergence of structure-related outcome measures as the primary means for assessing the effectiveness of antirheumatic agents, the regular use of X-rays is recommended for the continued monitoring and evaluation of patients. In addition to the control of symptoms and improvement in physical function, a reduction in erosions and joint-space narrowing should be considered among the goals of therapy, leading to a better quality of life. Adherence to therapy is an important element in optimizing outcomes. Durability of therapy with anti-TNF agents as reported from clinical trials can also be achieved in the clinical setting. Concomitant methotrexate therapy might be important in maintaining TNF antagonist therapy in the long term. Overall, the TNF antagonists have led to improvements in clinical and radiographic outcomes in patients with RA, especially those who have failed to show a complete response to methotrexate.
Figures

References
-
- Lard LR, Visser H, Speyer I, van der Horst-Bruinsma IE, Zwinderman AH, Breedveld FC, Hazes JM. Early versus delayed treatment in patients with recent-onset rheumatoid arthritis: comparison of two cohorts who received different treatment strategies. Am J Med. 2001;111:446–451. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9343(01)00872-5. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Arnett FC, Edworthy SM, Bloch DA, McShane DJ, Fries JF, Cooper NS, Healey LA, Kaplan SR, Liang MH, Luthra HS. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988;31:315–324. - PubMed
-
- van der Heide A, Jacobs JWG, Bijlsma JWJ, Heurkens AHM, van Booma-Frankfort C, van der Veen MJ, Haanen HC, Hofman DM. The effectiveness of early treatment with 'second-line' antirheumatic drugs. A randomized, controlled trial. Ann Intern Med. 1996;124:699–707. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

