Trends in Medicaid prescribed drug expenditures and utilization
- PMID: 15229997
- PMCID: PMC4194859
Trends in Medicaid prescribed drug expenditures and utilization
Abstract
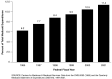
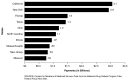
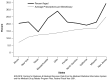
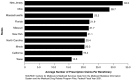
The findings show that with the development of a multitude of safe and effective drugs during the later part of the 20th century and the beginning of the 21st century, drugs are, as never before, a true mainstay of medical treatment. CMS continues to monitor drug utilization and expenditures in all of its programs in order to ensure that care is rendered in a cost-effective manner that is beneficial to the patient. This highlight summarizes trends in drug expenditures and utilization in the Medicaid Program.
Figures



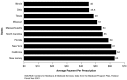
References
-
- Social Security Administration. Baltimore, Maryland: Compilation of the Social Security Laws Social Security Act, Section 1927(a)(1) Internet address: http://www.ssa.gov/OP_Home/ssact/title19/1927.htm (Accessed September 2003.)
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
