Interaction of St John's wort with conventional drugs: systematic review of clinical trials
- PMID: 15231618
- PMCID: PMC443448
- DOI: 10.1136/bmj.329.7456.27
Interaction of St John's wort with conventional drugs: systematic review of clinical trials
Abstract
Objective: To determine the methodological quality of clinical trials that examined possible interactions of St John's wort with conventional drugs, and to examine the results of these trials.
Design: Systematic review.
Data sources: Electronic databases from inception to April 2004, reference lists from published reports, and experts in the field.
Study selection: Eligible studies were prospective clinical trials evaluating the pharmacokinetic effect of St John's wort on the metabolism of conventional drugs.
Data extraction: Two reviewers selected studies for inclusion and independently extracted data.
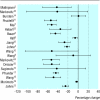
Data synthesis: 22 pharmacokinetic trials studied an average of 12 (SD 5) participants; 17 trials studied healthy volunteers and five studied patients. Most (17) studies used a "before and after" design; four studies used control groups other than the active group. Three studies randomised the sequence of administration or the participants to study arms or periods; three studies blinded participants or investigators. In 15 trials, investigators independently assayed the herb. Of 19 trials with available plasma data, three found no important interaction (change in area under the curve < 20%) and 17 found a decrease in systemic bioavailability of the conventional drug; in seven studies the 95% confidence interval excluded a decrease of < 20%.
Conclusion: Clinicians and patients should beware of possible decreases in the systemic bioavailability of conventional drugs when taken concomitantly with St John's wort.
Figures
Comment in
-
Adverse drug reactions as cause of admission to hospital: alcohol and other non-prescribed drugs may have impact on adverse drug reactions.BMJ. 2004 Aug 21;329(7463):459; author reply 460. doi: 10.1136/bmj.329.7463.459. BMJ. 2004. PMID: 15321915 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
The effect of St John's wort extracts on CYP3A: a systematic review of prospective clinical trials.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2006 Nov;62(5):512-26. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2006.02755.x. Epub 2006 Sep 29. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 17010103 Free PMC article.
-
St John's wort for depression.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005 Apr 18;(2):CD000448. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000448.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008 Oct 08;(4):CD000448. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000448.pub3. PMID: 15846605 Updated.
-
St John's wort for depression.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2000;(2):CD000448. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000448. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2000. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005 Apr 18;(2):CD000448. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000448.pub2. PMID: 10796719 Updated.
-
A systematic review and meta-analysis of Hypericum perforatum in depression: a comprehensive clinical review.Int Clin Psychopharmacol. 2001 Sep;16(5):239-52. doi: 10.1097/00004850-200109000-00001. Int Clin Psychopharmacol. 2001. PMID: 11552767
-
Interactions between herbal medicines and prescribed drugs: a systematic review.Drugs. 2001;61(15):2163-75. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200161150-00002. Drugs. 2001. PMID: 11772128
Cited by
-
Effects of treatment with a commercially available St John's Wort product (Movina) on cholesterol levels in patients with hypercholesterolemia treated with simvastatin.Scand J Prim Health Care. 2007 Sep;25(3):154-9. doi: 10.1080/02813430701442768. Scand J Prim Health Care. 2007. PMID: 17846933 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Adverse drug reactions as cause of admission to hospital: alcohol and other non-prescribed drugs may have impact on adverse drug reactions.BMJ. 2004 Aug 21;329(7463):459; author reply 460. doi: 10.1136/bmj.329.7463.459. BMJ. 2004. PMID: 15321915 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Clinical relevance of potential self-medication drug interactions in antineoplastic and immune-modulating therapy among online pharmacy customers.Ther Adv Drug Saf. 2023 Aug 24;14:20420986231188845. doi: 10.1177/20420986231188845. eCollection 2023. Ther Adv Drug Saf. 2023. PMID: 37636837 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of St John's wort and CYP2C9 genotype on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of gliclazide.Br J Pharmacol. 2008 Apr;153(7):1579-86. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0707685. Epub 2008 Jan 21. Br J Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18204476 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Extended Intake of Mulberry Leaf Extract Delayed Metformin Elimination via Inhibiting the Organic Cation Transporter 2.Pharmaceutics. 2020 Jan 7;12(1):49. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics12010049. Pharmaceutics. 2020. PMID: 31936070 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Thomas KJ, Nicholl JP, Coleman P. Use and expenditure on complementary medicine in England: a population based survey. Complement Ther Med 2001;9: 2-11. - PubMed
-
- Altman DG, Gardner MJ. Means and their differences. In: Altman DG, Bryant TN, Gardner MJ, eds. Statistics with confidence. Bristol: BMJ Publishing, 2000: 28-35.
-
- Food and Drug Administration. In vivo drug metabolism/drug interaction studies—study design, data analysis, and recommendations for dosing and labeling. 1999. www.fda.gov/cber/gdlns/metabol.pdf (accessed 20 May 2004)
-
- Johne A, Schmider J, Brockmoller J, Stadelmann AM, Stormer E, Bauer S, et al. Decreased plasma levels of amitriptyline and its metabolites on comedication with an extract from St John's wort (Hypericum perforatum). J Clin Psychopharmacol 2002;22: 46-54. - PubMed
-
- Mathijssen RH, Verweij J, de Bruijn P, Loos WJ, Sparreboom A. Effects of St John's wort on irinotecan metabolism. J Natl Cancer Inst 2002;94: 1247-9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
