A phylogeny of caenorhabditis reveals frequent loss of introns during nematode evolution
- PMID: 15231741
- PMCID: PMC442136
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.2639304
A phylogeny of caenorhabditis reveals frequent loss of introns during nematode evolution
Abstract
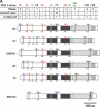
Since introns were discovered 26 years ago, people have wondered how changes in intron/exon structure occur, and what role these changes play in evolution. To answer these questions, we have begun studying gene structure in nematodes related to Caenorhabditis elegans. As a first step, we cloned a set of five genes from six different Caenorhabditis species, and used their amino acid sequences to construct the first detailed phylogeny of this genus. Our data indicate that nematode introns are lost at a very high rate during evolution, almost 400-fold higher than in mammals. These losses do not occur randomly, but instead, favor some introns and do not affect others. In contrast, intron gains are far less common than losses in these genes. On the basis of the sequences at each intron site, we suggest that several distinct mechanisms can cause introns to be lost. The small size of C. elegans introns should increase the rate at which each of these types of loss can occur, and might account for the dramatic difference in loss rate between nematodes and mammals.
Copyright 2004 Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press ISSN
Figures









References
-
- Baird, S.E., Sutherlin, M.E., and Emmons, S.W. 1992. Reproductive isolation in Rhabditidae (Nematoda:Secernentea); mechanisms that isolate six species of three genera. Evolution 46: 585–594. - PubMed
-
- Baldwin, J.G., Frisse, L.M., Vida, J.T., Eddleman, C.D., and Thomas, W.K. 1997. An evolutionary framework for the study of developmental evolution in a set of nematodes related to Caenorhabditis elegans. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 8: 249–259. - PubMed
-
- Blake, C.C. 1978. Do genes-in-pieces imply protein-in-pieces? Nature 273: 267–268.
-
- Blaxter, M.L., De Ley, P., Garey, J.R., Liu, L.X., Scheldeman, P., Vierstraete, A., Vanfleteren, J.R., Mackey, L.Y., Dorris, M., Frisse, L.M., et al. 1998. A molecular evolutionary framework for the phylum Nematoda. Nature 392: 71–75. - PubMed
-
- Blumenthal, T. and Steward, K. 1997. RNA processing and gene structure. In C. elegans II (eds. D.L. Riddle et al.), pp. 117–145. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
