Mauve: multiple alignment of conserved genomic sequence with rearrangements
- PMID: 15231754
- PMCID: PMC442156
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.2289704
Mauve: multiple alignment of conserved genomic sequence with rearrangements
Abstract
As genomes evolve, they undergo large-scale evolutionary processes that present a challenge to sequence comparison not posed by short sequences. Recombination causes frequent genome rearrangements, horizontal transfer introduces new sequences into bacterial chromosomes, and deletions remove segments of the genome. Consequently, each genome is a mosaic of unique lineage-specific segments, regions shared with a subset of other genomes and segments conserved among all the genomes under consideration. Furthermore, the linear order of these segments may be shuffled among genomes. We present methods for identification and alignment of conserved genomic DNA in the presence of rearrangements and horizontal transfer. Our methods have been implemented in a software package called Mauve. Mauve has been applied to align nine enterobacterial genomes and to determine global rearrangement structure in three mammalian genomes. We have evaluated the quality of Mauve alignments and drawn comparison to other methods through extensive simulations of genome evolution.
Copyright 2004 Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press ISSN
Figures
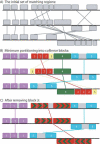



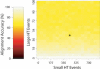

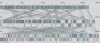
References
-
- Bader, D.A., Moret, B.M., and Yan, M. 2001. A linear-time algorithm for computing inversion distance between signed permutations with an experimental study. J. Comput. Biol. 8: 483–491. - PubMed
-
- Blanchette, M., Bourque, G., and Sankoff, D. 1997. Breakpoint phylogenies. Genome Inform Ser. Workshop Genome Inform. 8: 25–34. - PubMed
-
- Blattner, F.R., Plunkett III, G., Bloch, C.A., Perna, N.T., Burland, V., Riley, M., Collado-Vides, J., Glasner, J.D., Rode, C.K., Mayhew, G.F., et al. 1997. The complete genome sequence of Escherichia coli K-12. Science 277: 1453–1474. - PubMed
WEB SITE REFERENCES
-
- http://gel.ahabs.wisc.edu/mauve; the Mauve alignment system and visualization environment.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
