The Lactobacillus casei ptsHI47T mutation causes overexpression of a LevR-regulated but RpoN-independent operon encoding a mannose class phosphotransferase system
- PMID: 15231787
- PMCID: PMC438589
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.186.14.4543-4555.2004
The Lactobacillus casei ptsHI47T mutation causes overexpression of a LevR-regulated but RpoN-independent operon encoding a mannose class phosphotransferase system
Abstract
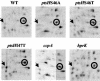
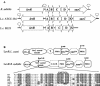
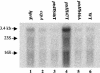
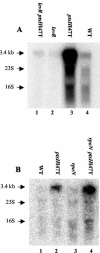
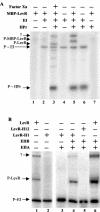
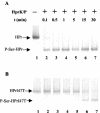
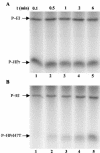
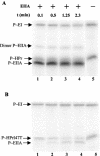
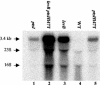
A proteome analysis of Lactobacillus casei mutants that are affected in carbon catabolite repression revealed that a 15-kDa protein was strongly overproduced in a ptsHI47T mutant. This protein was identified as EIIA of a mannose class phosphotransferase system (PTS). A 7.1-kb DNA fragment containing the EIIA-encoding open reading frame and five other genes was sequenced. The first gene encodes a protein resembling the RpoN (sigma54)-dependent Bacillus subtilis transcription activator LevR. The following pentacistronic operon is oriented in the opposite direction and encodes four proteins with strong similarity to the proteins of the B. subtilis Lev-PTS and one protein of unknown function. The genes present on the 7.1-kb DNA fragment were therefore called levR and levABCDX. The levABCDX operon was induced by fructose and mannose. No "-12, -24" promoter typical of RpoN-dependent genes precedes the L. casei lev operon, and its expression was therefore RpoN independent but required LevR. Phosphorylation of LevR by P approximately His-HPr stimulates its activity, while phosphorylation by P approximately EIIBLev inhibits it. Disruption of the EIIBLev-encoding levB gene therefore led to strong constitutive expression of the lev operon, which was weaker in a strain carrying a ptsI mutation preventing phosphorylation by both P approximately EIIBLev and P approximately His-HPr. Expression of the L. casei lev operon is also subject to P-Ser-HPr-mediated catabolite repression. The observed slow phosphoenolpyruvate- and ATP-dependent phosphorylation of HPrI47T as well as the slow phosphoryl group transfer from the mutant P approximately His-HPr to EIIALev are assumed to be responsible for the elevated expression of the lev operon in the ptsHI47T mutant.
Copyright 2004 American Society for Microbiology
Figures
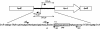
Similar articles
-
An esterase gene from Lactobacillus casei cotranscribed with genes encoding a phosphoenolpyruvate:sugar phosphotransferase system and regulated by a LevR-like activator and sigma54 factor.J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol. 2004;8(2):117-28. doi: 10.1159/000084567. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol. 2004. PMID: 15925903
-
The HPr protein of the phosphotransferase system links induction and catabolite repression of the Bacillus subtilis levanase operon.J Bacteriol. 1995 Dec;177(23):6928-36. doi: 10.1128/jb.177.23.6928-6936.1995. J Bacteriol. 1995. PMID: 7592487 Free PMC article.
-
Genetics of L-sorbose transport and metabolism in Lactobacillus casei.J Bacteriol. 2000 Jan;182(1):155-63. doi: 10.1128/JB.182.1.155-163.2000. J Bacteriol. 2000. PMID: 10613875 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription regulators potentially controlled by HPr kinase/phosphorylase in Gram-negative bacteria.J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol. 2003;5(4):206-15. doi: 10.1159/000071072. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol. 2003. PMID: 12867744 Review.
-
Phosphotransfer functions mutated Bacillus subtilis HPr-like protein Crh carrying a histidine in the active site.J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol. 2001 Jul;3(3):439-44. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol. 2001. PMID: 11361076 Review.
Cited by
-
CcpA represses the expression of the divergent cit operons of Enterococcus faecalis through multiple cre sites.BMC Microbiol. 2011 Oct 11;11:227. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-11-227. BMC Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21989394 Free PMC article.
-
Functional analysis of the fructooligosaccharide utilization operon in Lactobacillus paracasei 1195.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2007 Sep;73(18):5716-24. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00805-07. Epub 2007 Jul 20. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17644636 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction with enzyme IIBMpo (EIIBMpo) and phosphorylation by phosphorylated EIIBMpo exert antagonistic effects on the transcriptional activator ManR of Listeria monocytogenes.J Bacteriol. 2015 May;197(9):1559-72. doi: 10.1128/JB.02522-14. Epub 2015 Feb 17. J Bacteriol. 2015. PMID: 25691525 Free PMC article.
-
A generic approach to identify Transcription Factor-specific operator motifs; Inferences for LacI-family mediated regulation in Lactobacillus plantarum WCFS1.BMC Genomics. 2008 Mar 27;9:145. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-9-145. BMC Genomics. 2008. PMID: 18371204 Free PMC article.
-
Fine-tuned transcriptional regulation of malate operons in Enterococcus faecalis.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2012 Mar;78(6):1936-45. doi: 10.1128/AEM.07280-11. Epub 2012 Jan 13. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22247139 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Acedo-Félix, E., and G. Pérez-Martinez. 2003. Significant differences between Lactobacillus casei subsp. casei ATCC 393T and a commonly used plasmid-cured derivative revealed by a polyphasic study. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 53:67-75. - PubMed
-
- Ajdic, D., W. M. McShan, R. E. McLaughlin, G. Savic, J. Chang, M. B. Carson, C. Primeaux, R. Tian, S. Kenton, H. Jia, S. Lin, Y. Qian, S. Li, H. Zhu, F. Najar, H. Lai, J. White, B. A. Roe, and J. J. Ferretti. 2002. Genome sequence of Streptococcus mutans UA159, a cariogenic dental pathogen. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99:14434-14439. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Altschul, S. F., W. Gish, W. Miller, E. W. Myers, and D. J. Lipman. 1990. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 215:403-410. - PubMed
-
- Berthier, F., M. Zagorec, M. Champonmier-Vergès, S. D. Ehrlich, and F. Morel-Deville. 1996. Efficient transformation of Lactobacillus sake by electroporation. Microbiology 142:1273-1279. - PubMed
-
- Charrier, V., E. Buckley, D. Parsonage, A. Galinier, E. Darbon, M. Jaquinod, E. Forest, J. Deutscher, and A. Claiborne. 1997. Cloning and sequencing of two enterococcal glpK genes and regulation of the encoded glycerol kinases by phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent, phosphotransferase system-catalyzed phosphorylation of a single histidyl residue. J. Biol. Chem. 272:14166-14174. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

