Two C-P lyase operons in Pseudomonas stutzeri and their roles in the oxidation of phosphonates, phosphite, and hypophosphite
- PMID: 15231805
- PMCID: PMC438566
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.186.14.4730-4739.2004
Two C-P lyase operons in Pseudomonas stutzeri and their roles in the oxidation of phosphonates, phosphite, and hypophosphite
Abstract
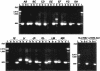
DNA sequencing and analysis of two distinct C-P lyase operons in Pseudomonas stutzeri WM88 were completed. The htxABCDEFGHIJKLMN operon encodes a hypophosphite-2-oxoglutarate dioxygenase (HtxA), whereas the predicted amino acid sequences of HtxB to HtxN are each homologous to the components of the Escherichia coli phn operon, which encodes C-P lyase, although homologs of E. coli phnF and phnO are absent. The genes in the htx operon are cotranscribed based on gene organization, and the presence of the intergenic sequences is verified by reverse transcription-PCR with total RNA. Deletion of the htx locus does not affect the ability of P. stutzeri to grow on phosphonates, indicating the presence of an additional C-P lyase pathway in this organism. To identify the genes comprising this pathway, a Deltahtx strain was mutagenized and one mutant lacking the ability to grow on methylphosphonate as the sole P source was isolated. A ca.-10.6-kbp region surrounding the transposon insertion site of this mutant was sequenced, revealing 13 open reading frames, designated phnCDEFGHIJKLMNP, which were homologous to the E. coli phn genes. Deletion of both the htx and phn operons of P. stutzeri abolishes all growth on methylphosphonate and aminoethylphosphonate. Both operons individually support growth on methylphosphonate; however, the phn operon supports growth on aminoethylphosphonate and phosphite, as well. The substrate ranges of both C-P lyases are limited, as growth on other phosphonate compounds, including glyphosate and phenylphosphonate, was not observed.
Copyright 2004 American Society for Microbiology
Figures
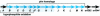
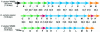
References
-
- Adams, F., and J. P. Conrad. 1953. Transition of phosphite to phosphate in soils. Soil Sci. 75:361-371.
-
- Ausubel, F. M., R. Brent, R. E. Kingston, D. D. Moore, J. G. Seidman, J. A. Smith, and K. Struhl. 1992. Current protocols in molecular biology. John Wiley & Sons, New York, N.Y.
-
- Chen, C. M., Q. Z. Ye, Z. M. Zhu, B. L. Wanner, and C. T. Walsh. 1990. Molecular biology of carbon-phosphorus bond cleavage. Cloning and sequencing of the phn (psiD) genes involved in alkylphosphonate uptake and C—P lyase activity in Escherichia coli B. J. Biol. Chem. 265:4461-4471. - PubMed
-
- Clark, L. L., E. D. Ingall, and R. Benner. 1999. Marine organic phosphorus cycling: novel insights from nuclear magnetic resonance. Am. J. Sci. 299:724-737.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

