Acute renal failure: definitions, diagnosis, pathogenesis, and therapy
- PMID: 15232604
- PMCID: PMC437979
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI22353
Acute renal failure: definitions, diagnosis, pathogenesis, and therapy
Erratum in
- J Clin Invest. 2004 Aug;114(4):598
Abstract
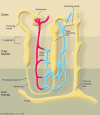
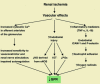
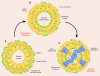
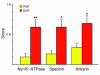
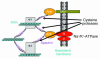
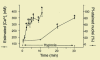
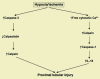
Acute renal failure (ARF), characterized by sudden loss of the ability of the kidneys to excrete wastes, concentrate urine, conserve electrolytes, and maintain fluid balance, is a frequent clinical problem, particularly in the intensive care unit, where it is associated with a mortality of between 50% and 80%. In this review, the epidemiology and pathophysiology of ARF are discussed, including the vascular, tubular, and inflammatory perturbations. The clinical evaluation of ARF and implications for potential future therapies to decrease the high mortality are described.
Figures
References
-
- Teschan PE, et al. Post-traumatic renal insufficiency in military casualties. I. Clinical characteristics. Am. J. Med. 1955;18:172–186. - PubMed
-
- Smith LH, Jr, et al. Post-traumatic renal insufficiency in military casualties. II. Management, use of an artificial kidney, prognosis. Am. J. Med. 1955;18:187–198. - PubMed
-
- Butkus DE. Post-traumatic acute renal failure in combat casualties: a historical review. Mil. Med. 1984;149:117–124. - PubMed
-
- Whelton A, Donadio JV., Jr Post-traumatic acute renal failure in Vietnam. A comparison with the Korean war experience. Johns Hopkins Med. J. 1969;124:95–105. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

