Neutrophil protein kinase Cdelta as a mediator of stroke-reperfusion injury
- PMID: 15232611
- PMCID: PMC437973
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI21655
Neutrophil protein kinase Cdelta as a mediator of stroke-reperfusion injury
Abstract
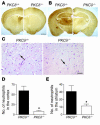
Thrombolysis is widely used to intervene in acute ischemic stroke, but reestablishment of circulation may paradoxically initiate a reperfusion injury. Here we describe studies with mice lacking protein kinase Cdelta (PKCdelta) showing that absence of this enzyme markedly reduces reperfusion injury following transient ischemia. This was associated with reduced infiltration of peripheral blood neutrophils into infarcted tissue and with impaired neutrophil adhesion, migration, respiratory burst, and degranulation in vitro. Total body irradiation followed by transplantation with bone marrow from PKCdelta-null mice donors reduced infarct size and improved neurological outcome in WT mice, whereas marrow transplantation from WT donors increased infarction and worsened neurological scores in PKCdelta-null mice. These results indicate an important role for neutrophil PKCdelta in reperfusion injury and strongly suggest that PKCdelta inhibitors could prove useful in the treatment of stroke.
Figures




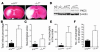
Similar articles
-
Protein kinase C isozymes in stroke.Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2005 Feb;15(2):47-51. doi: 10.1016/j.tcm.2005.01.003. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2005. PMID: 15885569 Review.
-
Cerebral protection in homozygous null ICAM-1 mice after middle cerebral artery occlusion. Role of neutrophil adhesion in the pathogenesis of stroke.J Clin Invest. 1996 Jan 1;97(1):209-16. doi: 10.1172/JCI118392. J Clin Invest. 1996. PMID: 8550836 Free PMC article.
-
Mice deficient in Mac-1 (CD11b/CD18) are less susceptible to cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury.Stroke. 1999 Jan;30(1):134-9. doi: 10.1161/01.str.30.1.134. Stroke. 1999. PMID: 9880401
-
The receptor for activated complement factor 5 (C5aR) conveys myocardial ischemic damage by mediating neutrophil transmigration.Immunobiology. 2013 Sep;218(9):1131-8. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2013.03.006. Epub 2013 Mar 28. Immunobiology. 2013. PMID: 23642836
-
Neutrophils--a key component of ischemia-reperfusion injury.Shock. 2013 Dec;40(6):463-70. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0000000000000044. Shock. 2013. PMID: 24088997 Review.
Cited by
-
Genetic disruption of protein kinase Cδ reduces endotoxin-induced lung injury.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2012 Nov 15;303(10):L880-8. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00169.2012. Epub 2012 Sep 14. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22983354 Free PMC article.
-
The Inflammatory Response After Ischemic Stroke: Targeting β2 and β1 Integrins.Front Neurosci. 2019 May 28;13:540. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2019.00540. eCollection 2019. Front Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31191232 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Significance of marrow-derived nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase in experimental ischemic stroke.Ann Neurol. 2011 Oct;70(4):606-15. doi: 10.1002/ana.22476. Ann Neurol. 2011. PMID: 22028221 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Programmed Death Ligand 1-AKT-engineered Mesenchymal Stem Cells Promote Neuroplasticity to Target Stroke Therapy.Mol Neurobiol. 2024 Jul;61(7):3819-3835. doi: 10.1007/s12035-023-03779-w. Epub 2023 Nov 29. Mol Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 38030932
-
Common mechanisms of Alzheimer's disease and ischemic stroke: the role of protein kinase C in the progression of age-related neurodegeneration.J Alzheimers Dis. 2015;43(3):711-24. doi: 10.3233/JAD-141422. J Alzheimers Dis. 2015. PMID: 25114088 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Stapf C, Mohr JP. Ischemic stroke therapy. Annu. Rev. Med. 2002;53:453–475. - PubMed
-
- Becker KJ. Targeting the central nervous system inflammatory response in ischemic stroke. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2001;14:349–353. - PubMed
-
- Emsley HC, Tyrrell PJ. Inflammation and infection in clinical stroke. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2002;22:1399–1419. - PubMed
-
- Jean WC, Spellman SR, Nussbaum ES, Low WC. Reperfusion injury after focal cerebral ischemia: the role of inflammation and the therapeutic horizon. Neurosurgery. 1998;43:1382–1396. - PubMed
-
- Cavanagh SP, Gough MJ, Homer-Vanniasinkam S. The role of the neutrophil in ischaemia-reperfusion injury: potential therapeutic interventions. Cardiovasc. Res. 1998;6:112–118. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

