Extracellular NAD+ regulates intracellular free calcium concentration in human monocytes
- PMID: 15233622
- PMCID: PMC1133960
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20040979
Extracellular NAD+ regulates intracellular free calcium concentration in human monocytes
Abstract
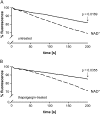
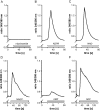
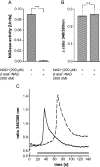
Ca(2+) ions play a critical role in the biochemical cascade of signal transduction pathways, leading to the activation of immune cells. In the present study, we show that the exposure of freshly isolated human monocytes to NAD(+) results in a rapid concentration-dependent elevation of [Ca(2+)](i) (intracellular free Ca(2+) concentration) caused by the influx of extracellular Ca(2+). NAD(+) derivatives containing a modified adenine or nicotinamide ring failed to trigger a Ca(2+) increase. Treating monocytes with ADPR (ADP-ribose), a major degradation product of NAD(+), also resulted in a rise in [Ca(2+)](i). Selective inhibition of CD38, an NAD-glycohydrolase that generates free ADPR from NAD(+), does not abolish the effect of NAD(+), excluding the possibility that NAD(+) might act via ADPR. The NAD(+)-induced Ca(2+) response was prevented by the prior addition of ADPR and vice versa, indicating that both compounds share some mechanisms mediating the rise in [Ca(2+)](i). NAD(+), as well as ADPR, were ineffective when applied following ATP, suggesting that ATP controls events that intersect with NAD(+) and ADPR signalling.
Figures
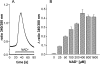

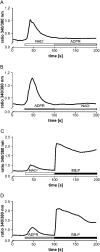
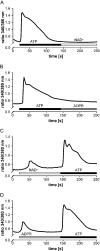
Comment in
-
NAD+ surfaces again.Biochem J. 2004 Sep 15;382(Pt 3):e5-6. doi: 10.1042/BJ20041217. Biochem J. 2004. PMID: 15352307 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wang J., Nemoto E., Kots A. Y., Kaslow H. R., Dennert G. Regulation of cytotoxic T cells by ecto-nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) correlates with cell surface GPI-anchored/arginine ADP-ribosyltransferase. J. Immunol. 1994;153:4048–4058. - PubMed
-
- Liu Z. X., Azhipa O., Okamoto S., Govindarajan S., Dennert G. Extracellular nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide induces T cell apoptosis in vivo and in vitro. J. Immunol. 2001;167:4942–4947. - PubMed
-
- Adriouch S., Ohlrogge W., Haag F., Koch-Nolte F., Seman M. Rapid induction of naive T cell apoptosis by ecto-nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide: requirement for mono(ADP-ribosyl)transferase 2 and a downstream effector. J. Immunol. 2001;167:196–203. - PubMed
-
- Bortell R., Moss J., McKenna R. C., Rigby M. R., Niedzwiecki D., Stevens L. A., Patton W. A., Mordes J. P., Greiner D. L., Rossini A. A. Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) and its metabolites inhibit T lymphocyte proliferation: role of cell surface NAD glycohydrolase and pyrophosphatase activities. J. Immunol. 2001;167:2049–2059. - PubMed
-
- Dubyak G. R. Role of P2 receptors in the immune system. In: Abbracchio M. P., Williams M., editors. Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology: Purinergic and Pyrimidinergic Signalling, vol. 151/II. Berlin: Springer-Verlag; 2001. p. 323.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

