Membrane-bound carboxypeptidase E facilitates the entry of eosinophil cationic protein into neuroendocrine cells
- PMID: 15233624
- PMCID: PMC1133959
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20040894
Membrane-bound carboxypeptidase E facilitates the entry of eosinophil cationic protein into neuroendocrine cells
Abstract
ECP (eosinophil cationic protein) is a major component of eosinophil granule proteins, and is used as a clinical biomarker for asthma and allergic inflammatory disease. ECP has been implicated in damage to the cell membrane of many tissue types, but the mechanism is not well known. In the present study, mECP-eGFP-6H, a recombinant fusion protein containing mature ECP (mECP), enhanced green fluorescence protein (eGFP) and a His(6) tag (6H), has been expressed, purified and added to GH3 neuroendocrine cells to study the internalization ability of ECP. We found that mECP-eGFP-6H entered into GH3 neuroendocrine cells and inhibited the growth of the cells with an IC(50) of 0.8 microM. By yeast two-hybrid screening and immunoprecipitation, we have identified a specific protein-protein interaction between mECP and CPE (carboxypeptidase E), a well characterized metalloprotease. Further in vivo yeast two-hybrid screening has also revealed that residues 318-387 located in a region of unknown function in mature CPE are indispensable for association with mECP. In addition, the uptake of mECP-eGFP-6H is suppressed by dominant-negative expression of the recycling defect mutant pre-pro-HA-CPE(S471A,E472A) in GH3 cells, suggesting that the entry of mECP-eGFP-6H is associated with the recycling of CPE in GH3 cells. Taken together, we have demonstrated that CPE possesses a novel function to facilitate the entry of ECP to neuroendocrine cells, and such an endocytotic process allows the cytotoxic ECP to inhibit growth of the target cells.
Figures

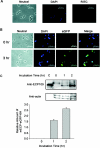
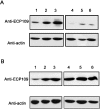


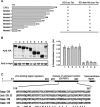
Similar articles
-
Signal peptide of eosinophil cationic protein upregulates transforming growth factor-alpha expression in human cells.J Cell Biochem. 2007 Apr 1;100(5):1266-75. doi: 10.1002/jcb.21120. J Cell Biochem. 2007. PMID: 17063486
-
Interaction between secretogranin III and carboxypeptidase E facilitates prohormone sorting within secretory granules.J Cell Sci. 2005 Oct 15;118(Pt 20):4785-95. doi: 10.1242/jcs.02608. J Cell Sci. 2005. PMID: 16219686
-
Luminal interaction of phogrin with carboxypeptidase E for effective targeting to secretory granules.Traffic. 2011 Apr;12(4):499-506. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2011.01159.x. Epub 2011 Feb 8. Traffic. 2011. PMID: 21210912
-
Eosinophil cationic protein: overview of biological and genetic features.DNA Cell Biol. 2012 Sep;31(9):1442-6. doi: 10.1089/dna.2012.1729. Epub 2012 Jul 30. DNA Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22845733 Review.
-
Biogenesis and transport of secretory granules to release site in neuroendocrine cells.J Mol Neurosci. 2009 Feb;37(2):151-9. doi: 10.1007/s12031-008-9098-y. Epub 2008 Jul 8. J Mol Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 18607778 Review.
Cited by
-
How peptide hormone vesicles are transported to the secretion site for exocytosis.Mol Endocrinol. 2008 Dec;22(12):2583-95. doi: 10.1210/me.2008-0209. Epub 2008 Jul 31. Mol Endocrinol. 2008. PMID: 18669645 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of the interactions between eosinophil cationic protein and airway epithelial cells by traditional Chinese herbs.BMC Syst Biol. 2010 Sep 13;4 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):S8. doi: 10.1186/1752-0509-4-S2-S8. BMC Syst Biol. 2010. PMID: 20840735 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional regulation of human eosinophil RNases by an evolutionary- conserved sequence motif in primate genome.BMC Mol Biol. 2007 Oct 11;8:89. doi: 10.1186/1471-2199-8-89. BMC Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17927842 Free PMC article.
-
Carboxypeptidase E cytoplasmic tail-driven vesicle transport is key for activity-dependent secretion of peptide hormones.Mol Endocrinol. 2008 Apr;22(4):989-1005. doi: 10.1210/me.2007-0473. Epub 2008 Jan 17. Mol Endocrinol. 2008. PMID: 18202146 Free PMC article.
-
Dissecting carboxypeptidase E: properties, functions and pathophysiological roles in disease.Endocr Connect. 2017 May;6(4):R18-R38. doi: 10.1530/EC-17-0020. Epub 2017 Mar 27. Endocr Connect. 2017. PMID: 28348001 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lehrer R. I., Szklarek D., Barton A., Ganz T., Hamann K. J., Gleich G. J. Antibacterial properties of eosinophil major basic protein and eosinophil cationic protein. J. Immunol. 1989;142:4428–4434. - PubMed
-
- Hamann K. J., Gleich G. J., Checkel J. L., Loegering D. A., McCall J. W., Barker R. L. In vitro killing of microfilariae of Brugia pahangi and Brugia malayi by eosinophil granule proteins. J. Immunol. 1990;144:3166–3173. - PubMed
-
- Hamann K. J., Barker R. L., Loegering D. A., Gleich G. J. Comparative toxicity of purified human eosinophil granule proteins for newborn larvae of Trichinella spiralis. J. Parasitol. 1987;73:523–529. - PubMed
-
- Motojima S., Frigas E., Loegering D. A., Gleich G. J. Toxicity of eosinophil cationic proteins for guinea pig tracheal epithelium in vitro. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1989;139:801–805. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

