Highly sensitive intramolecularly quenched fluorogenic substrates for renin based on the combination of L-2-amino-3-(7-methoxy-4-coumaryl)propionic acid with 2,4-dinitrophenyl groups at various positions
- PMID: 15233625
- PMCID: PMC1133981
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20040729
Highly sensitive intramolecularly quenched fluorogenic substrates for renin based on the combination of L-2-amino-3-(7-methoxy-4-coumaryl)propionic acid with 2,4-dinitrophenyl groups at various positions
Abstract
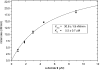
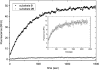
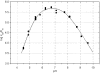
The development of renin inhibitors for the treatment of hypertension requires highly sensitive substrates to evaluate potency and to characterize the mechanism of tight-binding inhibitors. A series of intramolecularly quenched fluorogenic renin substrates, based on the N-terminal tetradecapeptide sequence of human angiotensinogen (hTDP), was synthesized using a solid-phase technique. Incorporation of the fluorescent amino acid L-Amp [L-2-amino-3-(7-methoxy-4-coumaryl)propionic acid] and the DNP (2,4-dinitrophenyl) group at various positions resulted in >90% quenching efficiency and strong product fluorescence. Shortening the hTDP sequence to an octapeptide from histidine in P5 to histidine in P3' (substrate 3) resulted in an acceptable k(cat)/K(m) (41000 M(-1).s(-1)) and further systematic variation gave substrate 9, DNP-Lys-His-Pro-Phe-His-Leu-Val-Ile-His-L-Amp, with a k(cat)/K(m) value of 350000 M(-1).s(-1) and 94% quenching efficiency. The free side chain of lysine, replacing the isoleucine residue at P6 position in the angiotensinogen sequence, contributed to the increased value for k(cat). The pH dependence of k(cat)/K(m) for renin and substrate 9 showed that the optimal pH is at pH 6-7. It also showed two titrating groups on the acidic side of the pH optimum, and one titrating group with a pK(a) of 7.8 on the alkaline side. The combination of good kinetic and spectroscopic properties resulted in a >20-fold improvement in the sensitivity of renin assay, compared with the commercial substrate Arg-Glu(EDANS)-Ile-His-Pro-Phe-His-Leu-Val-Ile-His-Thr-Lys(DABCYL)-Arg [where EDANS is 5-[(2-aminoethyl)amino]naphthalene-1-sulphonic acid and DABCYL is 4-(4-dimethylaminophenylazo)benzoic acid] (k(cat)/K(m)=268000 M(-1) x s(-1), quenching efficiency <80%). The detection limit in a microplate renin assay was 60 pM, making substrate 9 well suited for the evaluation of inhibitors at picomolar concentrations.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A continuous fluorescence assay of renin activity.Anal Biochem. 1993 May 1;210(2):351-9. doi: 10.1006/abio.1993.1207. Anal Biochem. 1993. PMID: 8512070
-
A quenched fluorescent substrate for thimet peptidase containing a new fluorescent amino acid, DL-2-amino-3-(7-methoxy-4-coumaryl)propionic acid.Biochem J. 1991 Feb 15;274 ( Pt 1)(Pt 1):45-8. doi: 10.1042/bj2740045. Biochem J. 1991. PMID: 2001250 Free PMC article.
-
Proton inventory studies of alpha-thrombin-catalyzed reactions of substrates with selected P and P' sites.J Am Chem Soc. 2004 May 19;126(19):6017-24. doi: 10.1021/ja0320166. J Am Chem Soc. 2004. PMID: 15137766
-
Exploiting the molecular template of angiotensinogen in the discovery and design of peptidyl, pseudopeptidyl and peptidimimetic inhibitors of human renin: a structure-activity perspective.Adv Exp Med Biol. 1991;306:307-23. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-6012-4_37. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1991. PMID: 1812721 Review. No abstract available.
-
Is renin a factor in the etiology of essential hypertension?Hypertension. 1983 Nov-Dec;5(6 Pt 3):V8-15. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.5.6_pt_3.v8. Hypertension. 1983. PMID: 6418650 Review.
Cited by
-
Discovery and characterization of a small-molecule enteropeptidase inhibitor, SCO-792.Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2019 Sep 4;7(5):e00517. doi: 10.1002/prp2.517. eCollection 2019 Oct. Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2019. PMID: 31508234 Free PMC article.
-
A fluorogenic near-infrared imaging agent for quantifying plasma and local tissue renin activity in vivo and ex vivo.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2012 Aug 15;303(4):F593-603. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00361.2011. Epub 2012 Jun 6. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22674025 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular fluorescence, phosphorescence, and chemiluminescence spectrometry.Anal Chem. 2006 Jun 15;78(12):4047-68. doi: 10.1021/ac060683m. Anal Chem. 2006. PMID: 16771540 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Coumarin as a structural component of substrates and probes for serine and cysteine proteases.Biochim Biophys Acta Proteins Proteom. 2020 Sep;1868(9):140445. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2020.140445. Epub 2020 May 13. Biochim Biophys Acta Proteins Proteom. 2020. PMID: 32405284 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Renin Activity in Heart Failure with Reduced Systolic Function-New Insights.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jun 28;20(13):3182. doi: 10.3390/ijms20133182. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31261774 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- He F. J., MacGregor G. A. Salt, blood pressure and the renin–angiotensin system. J. Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst. 2003;4:11–16. - PubMed
-
- De Gasparo M., Catt K. J., Inagami T., Wright J. W., Unger T. International Union of Pharmacology. XXIII. The angiotensin II receptors. Pharmacol. Rev. 2000;52:415–472. - PubMed
-
- Kaschina E., Unger T. Angiotensin AT1/AT2 receptors: regulation, signalling and function. Blood Pressure. 2003;12:70–88. - PubMed
-
- Waeber B., Nussberger J., Brunner H. R. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors in hypertension. In: Laragh J. H., Brenner B. M., editors. Hypertension: Pathophysiology, Diagnosis and Management. 2nd edn. New York: Raven Press; 1995. pp. 2861–2876.
-
- Taal M. W., Brenner B. M. Renoprotective benefits of RAS inhibition: from ACEI to angiotensin II antagonists. Kidney Int. 2000;57:1803–1817. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

