Development and evaluation of an efficient 3'-noncoding region based SARS coronavirus (SARS-CoV) RT-PCR assay for detection of SARS-CoV infections
- PMID: 15234807
- PMCID: PMC7119649
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2004.04.008
Development and evaluation of an efficient 3'-noncoding region based SARS coronavirus (SARS-CoV) RT-PCR assay for detection of SARS-CoV infections
Abstract
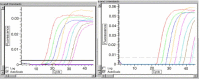
The severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) epidemic originating from China in 2002 was caused by a previously uncharacterized coronavirus that could be identified by specific RT-PCR amplification. Efforts to control future SARS outbreaks depend on the accurate and early identification of SARS-CoV infected patients. A real-time fluorogenic RT-PCR assay based on the 3'-noncoding region (3'-NCR) of SARS-CoV genome was developed as a quantitative SARS diagnostic tool. The ideal amplification efficiency of a sensitive SARS-CoV RT-PCR assay should yield an E value (PCR product concentration increase per amplification cycle) equal to 2.0. It was demonstrated that the 3'-NCR SARS-CoV based RT-PCR reactions could be formulated to reach excellent E values of 1.81, or 91% amplification efficacy. The SARS-CoV cDNA preparations derived from viral RNA extract and the cloned recombinant plasmid both exhibit the identical amplification characteristics, i.e. amplification efficacy using the same PCR formulation developed in this study. The viral genomic copy (or genomic equivalences, GE) per infectious unit (GE/pfu) of SARS-CoV used in this study was also established to be approximate 1200-1600:1. The assay's detection sensitivity could reach 0.005 pfu or 6-8 GE per assay. It was preliminarily demonstrated that the assay could efficiently detect SARS-CoV from clinical specimens of SARS probable and suspected patients identified in Taiwan. The 3'-NCR based SARS-CoV assay demonstrated 100% diagnostic specificity testing samples of patients with acute respiratory disease from a non-SARS epidemic region.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Detection of SARS coronavirus in patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome by conventional and real-time quantitative reverse transcription-PCR assays.Clin Chem. 2004 Jan;50(1):67-72. doi: 10.1373/clinchem.2003.023663. Clin Chem. 2004. PMID: 14709637 Free PMC article.
-
Real-time reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction assay for SARS-associated coronavirus.Emerg Infect Dis. 2004 Feb;10(2):311-6. doi: 10.3201/eid1002.030759. Emerg Infect Dis. 2004. PMID: 15030703 Free PMC article.
-
Coupling multiplex RT-PCR to a gene chip assay for sensitive and semiquantitative detection of severe acute respiratory syndrome-coronavirus.Lab Invest. 2004 Sep;84(9):1085-91. doi: 10.1038/labinvest.3700136. Lab Invest. 2004. PMID: 15195120 Free PMC article.
-
[Enhanced-real time PCR: a highly sensitive method for SARS-coronavirus detection].Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2006 Apr 18;38(2):211-3. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2006. PMID: 16617369 Review. Chinese.
-
[Detection of SARS coronavirus RNA].Nihon Rinsho. 2005 Dec;63 Suppl 12:366-71. Nihon Rinsho. 2005. PMID: 16416820 Review. Japanese. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Laboratory testing of SARS-CoV, MERS-CoV, and SARS-CoV-2 (2019-nCoV): Current status, challenges, and countermeasures.Rev Med Virol. 2020 May;30(3):e2106. doi: 10.1002/rmv.2106. Epub 2020 Apr 17. Rev Med Virol. 2020. PMID: 32302058 Free PMC article. Review.
-
At the crossroads of epidemiology and biology: Bridging the gap between SARS-CoV-2 viral strain properties and epidemic wave characteristics.Biochimie. 2023 Oct;213:54-65. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2023.03.006. Epub 2023 Mar 16. Biochimie. 2023. PMID: 36931337 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Performance of single-step gel-based reverse transcription-PCR (RT-PCR) assays equivalent to that of real-time RT-PCR assays for detection of the severe acute respiratory syndrome-associated coronavirus.J Clin Microbiol. 2005 Aug;43(8):4262-5. doi: 10.1128/JCM.43.8.4262-4265.2005. J Clin Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 16081995 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular diagnosis of severe acute respiratory syndrome: the state of the art.J Mol Diagn. 2005 Nov;7(5):551-9. doi: 10.1016/S1525-1578(10)60587-9. J Mol Diagn. 2005. PMID: 16258152 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterization of monoclonal antibody against SARS coronavirus nucleocapsid antigen and development of an antigen capture ELISA.J Virol Methods. 2005 Jul;127(1):46-53. doi: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2005.03.004. Epub 2005 Apr 19. J Virol Methods. 2005. PMID: 15893565 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bae H.-G, Nitsche A, Teichmann A, Biel S.S, Niedrig M. Detection of yellow fever virus: a comparison of quantitative real-time PCR and plaque assay. J. Virol. Meth. 2003;110:185–191. - PubMed
-
- Booth C.M, Matukas L.M, Tomlinson G.A, Rachlis A.R, Rose D.B, Dwosh H.A, Walmsley S.L, Mazzulli T, Avendano M, Derkach P, Ephtimios I.E, Kitai I, Mederski B.D, Shadowitz S.B, Gold W.L, Hawryluck L.A, Rea E, Chenkin J.S, Cescon D.W, Poutanen S.M, Detsky A.S. Clinical features and short-term outcomes of 144 patients with SARS in the greater Toronto area. JAMA. 2003;289:2801–2809. - PubMed
-
- CDC, 2003a. CDC update: outbreak of severe acute respiratory syndrome—worldwide. MMWR 52 (2003) 241–248. - PubMed
-
- CDC, 2003b. Severe acute respiratory syndrome—Singapore. MMWR 52 (2003) 405–411. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

