A novel function of insulin in rat dermis
- PMID: 15235083
- PMCID: PMC1665113
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2004.067751
A novel function of insulin in rat dermis
Abstract
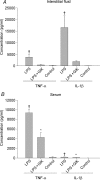
In this study we present a novel function of insulin in rat dermis. We investigated local effects of insulin on interstitial fluid pressure (Pif), and capillary albumin leakage and pro-inflammatory cytokine production in skin and serum after intravenous lipopolysaccharide (LPS), tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) and interleukin-1beta (IL-1beta) challenge treated with a glucose-insulin-potassium regimen (GIK). The main objective for this study was to investigate anti-inflammatory effects of insulin. Work by others shows that insulin stimulates cell adhesion, and that this effect is dependent upon phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) activity. Cytokines like platelet-derived growth factor BB (PDGF-BB) attenuate lowering of Pif, possibly via PI3K. LPS and pro-inflammatory cytokines contribute to oedema development during acute inflammation by lowering the Pif. Intravenous injection of LPS, TNF-alpha or IL-1beta to Wistar Møller rats caused a lowering of Pif, but after local injection of insulin in the paw, Pif increased back to control values. IL-1beta caused a lowering in control from -0.5 +/- 0.2 mmHg to -3.0 +/- 0.2 mmHg after 20 min (mean +/- S.E.M.) (P < 0.05). Within 50 min after insulin injection the pressure was increased to -0.6 +/- 0.2 mmHg (P > 0.05 compared with control). Insulin was given together with a PI3K inhibitor (wortmannin) locally in the skin, almost abolishing the effect of insulin on Pif. A GIK regimen was given as a continuous intravenous infusion, significantly attenuating the oedema formation after LPS or TNF-alpha/IL-1beta challenge. The same GIK regimen caused a significant reduction in pro-inflammatory cytokines in serum and in interstitial fluid in skin of endotoxaemic rats. These experiments show a possible role for insulin in the interstitium during inflammation induced by LPS and TNF-alpha/IL-1beta. Insulin can attenuate a lowering of Pif possibly via PI3K, and it has an anti-inflammatory effect by inhibiting production of pro-inflammatory cytokines.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Differential cytokine response in interstitial fluid in skin and serum during experimental inflammation in rats.J Physiol. 2004 Apr 1;556(Pt 1):193-202. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2003.057216. Epub 2004 Jan 14. J Physiol. 2004. PMID: 14724215 Free PMC article.
-
The influence of antibodies to TNF-alpha and IL-1beta on haemodynamic responses to the cytokines, and to lipopolysaccharide, in conscious rats.Br J Pharmacol. 1998 Dec;125(7):1543-50. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0702250. Br J Pharmacol. 1998. PMID: 9884083 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of the cytoskeletal fixation agent phalloidin on transcapillary albumin transport and interstitial fluid pressure following subdermal prostaglandin E1 administration in the rat.Acta Physiol Scand. 2004 Feb;180(2):125-32. doi: 10.1046/j.0001-6772.2003.01221.x. Acta Physiol Scand. 2004. PMID: 14738471
-
Insulin regulates cytokines and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 gene expression through nuclear factor-kappaB activation in LPS-induced acute lung injury in rats.Shock. 2009 Apr;31(4):404-9. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0b013e318186275e. Shock. 2009. PMID: 18791499
-
Effect of alpha-trinositol on interstitial fluid pressure, oedema generation and albumin extravasation in experimental frostbite in the rat.Br J Pharmacol. 1999 Mar;126(6):1367-74. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0702442. Br J Pharmacol. 1999. PMID: 10217530 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Early diabetic neuropathy: triggers and mechanisms.World J Gastroenterol. 2007 Jan 14;13(2):175-91. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i2.175. World J Gastroenterol. 2007. PMID: 17226897 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Modern View of the Interstitial Space in Health and Disease.Front Vet Sci. 2020 Nov 5;7:609583. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2020.609583. eCollection 2020. Front Vet Sci. 2020. PMID: 33251275 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adipocyte, adipose tissue, and infectious disease.Infect Immun. 2007 Mar;75(3):1066-78. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01455-06. Epub 2006 Nov 21. Infect Immun. 2007. PMID: 17118983 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Integrin alphavbeta3 acts downstream of insulin in normalization of interstitial fluid pressure in sepsis and in cell-mediated collagen gel contraction.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2008 Aug;295(2):H555-60. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00161.2008. Epub 2008 Jun 13. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18552165 Free PMC article.
-
Increased fibrosis and interstitial fluid pressure in two different types of syngeneic murine carcinoma grown in integrin β3-subunit deficient mice.PLoS One. 2012;7(3):e34082. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0034082. Epub 2012 Mar 30. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22479530 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahlen K, Berg A, Stiger F, Tengholm A, Siegbahn A, Gylfe E, Reed RK, Rubin K. Cell interactions with collagen matrices in vivo and in vitro depend on phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and free cytoplasmic calcium. Cell Adhes Commun. 1998;5:461–473. - PubMed
-
- Altavilla D, Saitta A, Guarini S, Galeano M, Squadrito G, Santamaria LB, Venuti FS, Bazzani C, Bertolini A, Squadrito F. Nuclear factor-kappaB as a target of cyclosporin in acute hypovolemic hemorrhagic shock. Cardiovasc Res. 2001;52:143–152. - PubMed
-
- Aukland K, Wiig H, Tenstad O, Renkin EM. Interstitial exclusion of macromolecules studied by graded centrifugation of rat tail tendon. Am J Physiol. 1997;273:H2794–H2803. - PubMed
-
- Berg A. Modulation of Interstitial Fluid Pressure by Connective Tissue Cells. 1999. PhD Thesis, Department of Physiology, University of Bergen, Bergen, Norway.
-
- Booth G, Stalker TJ, Lefer AM, Scalia R. Elevated ambient glucose induces acute inflammatory events in the microvasculature: effects of insulin. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2001;280:E848–E856. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

