Muscarinic modulation of erg potassium current
- PMID: 15235086
- PMCID: PMC1665067
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2004.066944
Muscarinic modulation of erg potassium current
Abstract
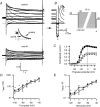
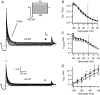
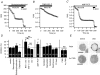
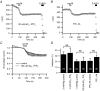
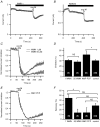
We studied modulation of current in human embryonic kidney tsA-201 cells coexpressing rat erg1 channels with M(1) muscarinic receptors. Maximal current was inhibited 30% during muscarinic receptor stimulation, with a small positive shift of the midpoint of activation. Inhibition was attenuated by coexpression of the regulator of G-protein signalling RGS2 or of a dominant-negative protein, G(q), but not by N-ethylmaleimide or C3 toxin. Overexpression of a constitutively active form of G(q) (but not of G(13) or of G(s)) abolished the erg current. Hence it is likely that G(q/11), and not G(i/o) or G(13), mediates muscarinic inhibition. Muscarinic suppression of erg was attenuated by chelating intracellular Ca(2+) to < 1 nm free Ca(2+) with 20 mm BAPTA in the pipette, but suppression was normal if internal Ca(2+) was strongly clamped to a 129 nm free Ca(2+) level with a BAPTA buffer and this was combined with numerous other measures to prevent intracellular Ca(2+) transients (pentosan polysulphate, preincubation with thapsigargin, and removal of extracellular Ca(2+)). Hence a minimum amount of Ca(2+) was necessary for the inhibition, but a Ca(2+) elevation was not. The ATP analogue AMP-PCP did not prevent inhibition. The protein kinase C (PKC) blockers staurosporine and bisindolylmaleimide I did not prevent inhibition, and the PKC-activating phorbol ester PMA did not mimic it. Neither the tyrosine kinase inhibitor genistein nor the tyrosine phosphatase inhibitor dephostatin prevented inhibition by oxotremorine-M. Hence protein kinases are not needed. Experiments with a high concentration of wortmannin were consistent with recovery being partially dependent on PIP(2) resynthesis. Wortmannin did not prevent muscarinic inhibition. Our studies of muscarinic inhibition of erg current suggest a role for phospholipase C, but not the classical downstream messengers, such as PKC or a calcium transient.
Figures
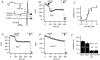
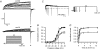
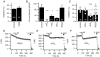

Similar articles
-
Muscarinic M(1) modulation of N and L types of calcium channels is mediated by protein kinase C in neostriatal neurons.Neuroscience. 2008 Sep 9;155(4):1079-97. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.06.047. Epub 2008 Jul 1. Neuroscience. 2008. PMID: 18644425
-
Muscarinic receptor-mediated excitation of rat intracardiac ganglion neurons.Neuropharmacology. 2015 Aug;95:395-404. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2015.04.014. Epub 2015 Apr 29. Neuropharmacology. 2015. PMID: 25937214
-
Modulation of hERG potassium currents in HEK-293 cells by protein kinase C. Evidence for direct phosphorylation of pore forming subunits.J Physiol. 2007 Jun 1;581(Pt 2):479-93. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2006.123414. Epub 2007 Mar 15. J Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17363390 Free PMC article.
-
Reconstitution of muscarinic modulation of the KCNQ2/KCNQ3 K(+) channels that underlie the neuronal M current.J Neurosci. 2000 Mar 1;20(5):1710-21. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.20-05-01710.2000. J Neurosci. 2000. PMID: 10684873 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of muscarinic m5 receptors inhibits recombinant KCNQ2/KCNQ3 K+ channels expressed in HEK293T cells.Eur J Pharmacol. 2003 Feb 21;462(1-3):25-32. doi: 10.1016/s0014-2999(03)01323-2. Eur J Pharmacol. 2003. PMID: 12591092
Cited by
-
Erg K+ currents modulate excitability in mouse mitral/tufted neurons.Pflugers Arch. 2009 Nov;459(1):55-70. doi: 10.1007/s00424-009-0709-4. Epub 2009 Aug 18. Pflugers Arch. 2009. PMID: 19688350
-
Specificity of TRH receptor coupling to G-proteins for regulation of ERG K+ channels in GH3 rat anterior pituitary cells.J Physiol. 2005 Aug 1;566(Pt 3):717-36. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2005.085803. Epub 2005 May 19. J Physiol. 2005. PMID: 15905217 Free PMC article.
-
Selective attenuation of Ether-a-go-go related K+ currents by endogenous acetylcholine reduces spike-frequency adaptation and network correlation.Elife. 2019 Apr 29;8:e44954. doi: 10.7554/eLife.44954. Elife. 2019. PMID: 31032798 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate interactions with the HERG K(+) channel.Pflugers Arch. 2007 Oct;455(1):105-13. doi: 10.1007/s00424-007-0292-5. Epub 2007 Jul 11. Pflugers Arch. 2007. PMID: 17622552 Review.
-
Modulation of Ether-à-Go-Go Related Gene (ERG) Current Governs Intrinsic Persistent Activity in Rodent Neocortical Pyramidal Cells.J Neurosci. 2018 Jan 10;38(2):423-440. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1774-17.2017. Epub 2017 Nov 24. J Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29175952 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barros F, Mieskes G, del Camino D, de la Peña P. Protein phosphatase 2A reverses inhibition of inward rectifying K+ currents by thyrotropin-releasing hormone in GH3 pituitary cells. FEBS Lett. 1993;336:433–439. - PubMed
-
- Bauer CK, Schäfer R, Schiemann D, Reid G, Hanganu I, Schwarz JR. A functional role of the erg-like inward rectifying K+ current in prolactin secretion from rat lactotrophs. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1999;148:37–45. - PubMed
-
- Bauer CK, Schwarz JR. Physiology of EAG K+ channels. J Membr Biol. 2001;182:1–15. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

