Signal peptide-dependent targeting of a rice alpha-amylase and cargo proteins to plastids and extracellular compartments of plant cells
- PMID: 15235120
- PMCID: PMC519054
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.104.042184
Signal peptide-dependent targeting of a rice alpha-amylase and cargo proteins to plastids and extracellular compartments of plant cells
Abstract
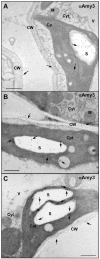
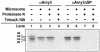
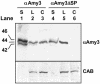
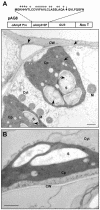
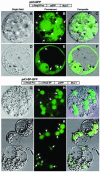
alpha-Amylases are important enzymes for starch degradation in plants. However, it has been a long-running debate as to whether alpha-amylases are localized in plastids where starch is stored. To study the subcellular localization of alpha-amylases in plant cells, a rice (Oryza sativa) alpha-amylase, alphaAmy3, with or without its own signal peptide (SP) was expressed in transgenic tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum) and analyzed. Loss-of-function analyses revealed that SP was required for targeting of alphaAmy3 to chloroplasts and/or amyloplasts and cell walls and/or extracellular compartments of leaves and suspension cells. SP was also required for in vitro transcribed and/or translated alphaAmy3 to be cotranslationally imported and processed in canine microsomes. alphaAmy3, present in chloroplasts of transgenic tobacco leaves, was processed to a product with Mr similar to alphaAmy3 minus its SP. Amino acid sequence analysis revealed that the SP of chloroplast localized alphaAmy3 was cleaved at a site only one amino acid preceding the predicted cleavage site. Function of the alphaAmy3 SP was further studied by gain-of-function analyses. beta-Glucuronidase (GUS) and green fluorescence protein fused with or without the alphaAmy3 SP was expressed in transgenic tobacco or rice. The alphaAmy3 SP directed translocation of GUS and green fluorescence protein to chloroplasts and/or amyloplasts and cell walls in tobacco leaves and rice suspension cells. The SP of another rice alpha-amylase, alphaAmy8, similarly directed the dual localizations of GUS in transgenic tobacco leaves. This study is the first evidence of SP-dependent dual translocations of proteins to plastids and extracellular compartments, which provides new insights into the role of SP in protein targeting and the pathways of SP-dependent protein translocation in plants.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Involvement of alpha-amylase I-1 in starch degradation in rice chloroplasts.Plant Cell Physiol. 2005 Jun;46(6):858-69. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pci091. Epub 2005 Apr 8. Plant Cell Physiol. 2005. PMID: 15821023
-
A CCR4 Association Factor 1, OsCAF1B, Participates in the αAmy3 mRNA Poly(A) Tail Shortening and Plays a Role in Germination and Seedling Growth.Plant Cell Physiol. 2020 Mar 1;61(3):554-564. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcz221. Plant Cell Physiol. 2020. PMID: 31782784
-
The rice alpha-amylase glycoprotein is targeted from the Golgi apparatus through the secretory pathway to the plastids.Plant Cell. 2009 Sep;21(9):2844-58. doi: 10.1105/tpc.109.068288. Epub 2009 Sep 18. Plant Cell. 2009. PMID: 19767453 Free PMC article.
-
The chloroplast protein import machinery: a review.Methods Mol Biol. 2010;619:307-21. doi: 10.1007/978-1-60327-412-8_18. Methods Mol Biol. 2010. PMID: 20419418 Review.
-
One ticket for multiple destinations: dual targeting of proteins to distinct subcellular locations.Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2003 Dec;6(6):589-95. doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2003.09.008. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2003. PMID: 14611958 Review.
Cited by
-
In Planta Functional Analysis and Subcellular Localization of the Oomycete Pathogen Plasmopara viticola Candidate RXLR Effector Repertoire.Front Plant Sci. 2018 Apr 13;9:286. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2018.00286. eCollection 2018. Front Plant Sci. 2018. PMID: 29706971 Free PMC article.
-
The Major Peanut Allergen Ara h 2 Produced in Nicotiana benthamiana Contains Hydroxyprolines and Is a Viable Alternative to the E. Coli Product in Allergy Diagnosis.Front Plant Sci. 2021 Oct 4;12:723363. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.723363. eCollection 2021. Front Plant Sci. 2021. PMID: 34671372 Free PMC article.
-
HS1 Is Involved in Hygromycin Resistance Through Facilitating Hygromycin Phosphotransferase Transportation From Cytosol to Chloroplast.Front Plant Sci. 2020 May 27;11:613. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2020.00613. eCollection 2020. Front Plant Sci. 2020. PMID: 32528495 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative analysis of predicted plastid-targeted proteomes of sequenced higher plant genomes.PLoS One. 2014 Nov 13;9(11):e112870. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0112870. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25393533 Free PMC article.
-
Production of recombinant proteins through sequestration in chloroplasts: a strategy based on nuclear transformation and post-translational protein import.Plant Cell Rep. 2019 Jul;38(7):825-833. doi: 10.1007/s00299-019-02431-z. Epub 2019 May 28. Plant Cell Rep. 2019. PMID: 31139894 Review.
References
-
- Beck E, Ziegler P (1989) Biosynthesis and degradation of starch in higher plants. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 40: 95–117
-
- Chan M-T, Chao Y-C, Yu S-M (1994) Novel gene expression system for plant cells based on induction of alpha-amylase promoter by carbohydrate starvation. J Biol Chem 269: 17635–17641 - PubMed
-
- Chen M-H, Liu L-F, Chen Y-R, Wu H-K, Yu S-M (1994) Expression of alpha-amylases, carbohydrate metabolism, and autophagy in cultured rice cells is coordinately regulated by sugar nutrient. Plant J 6: 625–636 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

