Importance of ERK1/2 in upregulation of endothelin type B receptors in cerebral arteries
- PMID: 15237095
- PMCID: PMC1575172
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705803
Importance of ERK1/2 in upregulation of endothelin type B receptors in cerebral arteries
Abstract
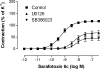
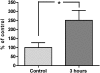
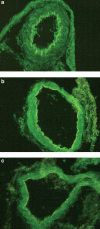
This study examines the importance of mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) in upregulation of endothelin type B (ETB) receptors. Rat middle cerebral arteries (MCAs) were incubated for 24 h with or without kinase inhibitors. Vessel segments were mounted in myographs and the contractile responses to endothelin-1 (ET-1; ETA and ETB receptor agonist) and sarafotoxin 6c (S6c; ETB receptor agonist) were studied. We used real-time PCR to measure the receptor mRNA levels. An ELISA assay showed the activation of ERK1/2 kinases after 3 h. Immunohistochemistry revealed the presence of ETB receptors on the vessels. After organ culture, S6c induced vasoconstriction. Incubation with the MEK/ERK inhibitors U0126 and SB386023 diminished the contractile response to S6c. The p38 MAPK inhibitor SB239063 did not affect the S6c-induced contraction. The ET-1-induced vasoconstriction was increased after incubation with SB386023 or SB239063, while unaffected by U0126. The ETB receptor mRNA levels were diminished by SB386023 and U0126. The ETA receptor mRNA levels were unaffected. The levels of activated ERK1/2 kinases were significantly higher after 3 h of organ culture as compared to fresh vessels. The level of ETB receptor protein on the smooth muscle cells of the MCA, visualised by immunohistochemistry, was somewhat diminished by SB386023. Our results show that the ERK1/2 MAPK is important in the upregulation of contractile ETB receptors in MCA after organ culture. Since there is a similar upregulation in models of focal ischaemia and subarachnoid haemorrhage, this may be an important pathophysiological event.
Copyright 2004 Nature Publishing Group
Figures
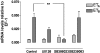
Similar articles
-
[ERK1/2 pathway involved in the expression of ETB receptors of the culturing smooth muscle cells of rat mesenteric artery].Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2006 Mar;41(3):257-62. Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2006. PMID: 16758999 Chinese.
-
Rapid functional upregulation of vasocontractile endothelin ETB receptors in rat coronary arteries.Life Sci. 2012 Oct 15;91(13-14):593-9. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2012.02.009. Epub 2012 Feb 25. Life Sci. 2012. PMID: 22391414
-
Intracellular pathways involved in upregulation of vascular endothelin type B receptors in cerebral arteries of the rat.Stroke. 2003 Jun;34(6):1479-83. doi: 10.1161/01.STR.0000072984.79136.79. Epub 2003 May 15. Stroke. 2003. PMID: 12750545
-
Upregulation of contractile endothelin type B receptors by lipid-soluble cigarette smoking particles in rat cerebral arteries via activation of MAPK.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2010 Nov 15;249(1):25-32. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2010.08.010. Epub 2010 Aug 15. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20716444
-
Late cerebral ischaemia after subarachnoid haemorrhage: is cerebrovascular receptor upregulation the mechanism behind?Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2011 Sep;203(1):209-24. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.2010.02227.x. Epub 2011 Feb 1. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2011. PMID: 21087418 Review.
Cited by
-
Minimally modified LDL upregulates endothelin type A receptors in rat coronary arterial smooth muscle cells.Mediators Inflamm. 2013;2013:656570. doi: 10.1155/2013/656570. Epub 2013 Jun 19. Mediators Inflamm. 2013. PMID: 23861561 Free PMC article.
-
MEK1/2 inhibition attenuates vascular ETA and ETB receptor alterations after cerebral ischaemia.Exp Brain Res. 2007 Apr;178(4):470-6. doi: 10.1007/s00221-006-0753-7. Epub 2006 Nov 8. Exp Brain Res. 2007. PMID: 17091294
-
Independent and synergistic roles of MEK-ERK1/2 and PKC pathways in regulating functional changes in vascular tissue following flow cessation.J Mol Cell Cardiol Plus. 2025 Apr 30;12:100300. doi: 10.1016/j.jmccpl.2025.100300. eCollection 2025 Jun. J Mol Cell Cardiol Plus. 2025. PMID: 40395439 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of cerebrovascular raf activation attenuates cerebral blood flow and prevents upregulation of contractile receptors after subarachnoid hemorrhage.BMC Neurosci. 2011 Oct 27;12:107. doi: 10.1186/1471-2202-12-107. BMC Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 22032648 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid-soluble cigarette smoking particles induce expression of inflammatory and extracellular-matrix-related genes in rat cerebral arteries.Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2009;5(1):333-41. doi: 10.2147/vhrm.s4866. Epub 2009 Apr 8. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2009. PMID: 19436652 Free PMC article.
References
-
- BARONE F.C., IRVING E.A., RAY A.M., LEE J.C., KASSIS S., KUMAR S., BADGER A.M., LEGOS J.J., ERHARDT J.A., OHLSTEIN E.H., HUNTER A.J., HARRISON D.C., PHILPOTT K., SMITH B.R., ADAMS J.L., PARSONS A.A. Inhibition of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase provides neuroprotection in cerebral focal ischemia. Med. Res. Rev. 2001;21:129–145. - PubMed
-
- BOULTON T.G., NYE S.H., ROBBINS D.J., IP N.Y., RADZIEJEWSKA E., MORGENBESSER S.D., DEPINHO R.A., PANAYOTATOS N., COBB M.H., YANCOPOULOS G.D. ERKs: a family of protein-serine/threonine kinases that are activated and tyrosine phosphorylated in response to insulin and NGF. Cell. 1991;65:663–675. - PubMed
-
- DAVIS S.M., LEES K.R., ALBERS G.W., DIENER H.C., MARKABI S., KARLSSON G., NORRIS J. Selfotel in acute ischemic stroke: possible neurotoxic effects of an NMDA antagonist. Stroke. 2000;31:347–354. - PubMed
-
- DIECKE F.P., BEYER-MEARS A. A mechanism for regulatory volume decrease in cultured lens epithelial cells. Curr. Eye Res. 1997;16:279–288. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

