Growth inhibition and apoptosis induction of tanshinone II-A on human hepatocellular carcinoma cells
- PMID: 15237427
- PMCID: PMC4572326
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i14.2024
Growth inhibition and apoptosis induction of tanshinone II-A on human hepatocellular carcinoma cells
Abstract
Aim: To evaluate the effects of tanshinone II-A on inducing growth inhibition and apoptosis of human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells.
Methods: The human hepatocellular carcinoma cell line SMMC-7721 was used for the study. The cells were treated with tanshinone II-A at different doses and different times. Cell growth and proliferation were measured by MTT assay, cell count and colony-forming assay. Apoptosis induction was detected by microscopy, DNA ladder electrophoresis and flow cytometry.
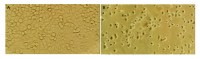
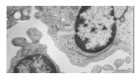
Results: In MTT assay, the inhibitory effect became gradually stronger with the passage of time, 24, 48, 72 and 96 h after treatment with tanshinone II-A, and the most significant effect was observed at 72 h. On the other hand, the increase of doses (0.125, 0.25, 0.5, 1.0 mg/L tanshinone II-A) resulted in enhanced inhibitory effect. The growth and proliferation of SMMC-7721 cells were obviously suppressed in a dose- and time-dependent manner. The results of cell count were similar to that of MTT assay. In colony-forming assay, the colony-forming rates were obviously inhibited by tanshinone II-A. In tanshinone II-A group, the morphology of cellular growth inhibition and characteristics of apoptosis such as chromatin condensation, crescent formation, margination and apoptotic body were observed under light and transmission electron microscopes. DNA ladder of cells was presented in electrophoresis. The apoptosis index (AI) was 16.9% (the control group was 4.6%) in flow cytometry. The cells were arrested in G(0)/G(1) phase, and the expressions of apoptosis-related genes bcl-2 and c-myc were down-regulated and fas, bax, p53 up-regulated.
Conclusion: Tanshinone II-A could inhibit the growth and proliferation of HCC cell effectively in vitro by apoptosis induction, which was associated with up-regulation of fas, p53, bax, expression and down-regulation of bcl-2 and c-myc.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Growth inhibition and apoptosis induction in human hepatoma cells by tanshinone II A.J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2003;23(2):166-8, 172. doi: 10.1007/BF02859946. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2003. PMID: 12973939
-
[Inhibition of cell growth and induction of apoptosis in human hepatoma cell line HepG2 by tanshione IIA].Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2007 Feb;32(1):99-103. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2007. PMID: 17344596 Chinese.
-
[Effect of Tanshinone II A on expression of EGF and EGFR in hepatocellular carcinoma cell line SMMC-7721].Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2009 Mar;38(2):163-9. doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-9292.2009.02.008. Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2009. PMID: 19363824 Chinese.
-
Preventive and therapeutic role of Tanshinone ⅡA in hepatology.Biomed Pharmacother. 2019 Apr;112:108676. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.108676. Epub 2019 Feb 21. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019. PMID: 30797157 Review.
-
[Progress in research of traditional Chinese medicine in inducing differentiation of human hepatoma cells].Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Xue Bao. 2007 Jan;5(1):92-6. doi: 10.3736/jcim20070119. Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Xue Bao. 2007. PMID: 17214945 Review. Chinese. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
An NQO1-initiated and p53-independent apoptotic pathway determines the anti-tumor effect of tanshinone IIA against non-small cell lung cancer.PLoS One. 2012;7(7):e42138. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0042138. Epub 2012 Jul 27. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22848731 Free PMC article.
-
Tanshinone IIA Inhibits Growth of Keratinocytes through Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis: Underlying Treatment Mechanism of Psoriasis.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2012;2012:927658. doi: 10.1155/2012/927658. Epub 2011 Nov 16. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2012. PMID: 22203883 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-hepatoma activity and mechanism of ursolic acid and its derivatives isolated from Aralia decaisneana.World J Gastroenterol. 2006 Feb 14;12(6):874-9. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i6.874. World J Gastroenterol. 2006. PMID: 16521214 Free PMC article.
-
Tanshinone IIA induces apoptosis in human oral cancer KB cells through a mitochondria-dependent pathway.Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:540516. doi: 10.1155/2014/540516. Epub 2014 May 13. Biomed Res Int. 2014. Retraction in: Biomed Res Int. 2017;2017:9496485. doi: 10.1155/2017/9496485. PMID: 24900970 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Anticancer Effects of Salvia miltiorrhiza Alcohol Extract on Oral Squamous Carcinoma Cells.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2017;2017:5364010. doi: 10.1155/2017/5364010. Epub 2017 Jan 29. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2017. PMID: 28246540 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kanzler S, Galle PR. Apoptosis and the liver. Semin Cancer Biol. 2000;10:173–184. - PubMed
-
- Carson DA, Ribeiro JM. Apoptosis and disease. Lancet. 1993;341:1251–1254. - PubMed
-
- Kerr JF, Winterford CM, Harmon BV. Apoptosis. Its significance in cancer and cancer therapy. Cancer. 1994;73:2013–2026. - PubMed
-
- Thompson CB. Apoptosis in the pathogenesis and treatment of disease. Science. 1995;267:1456–1462. - PubMed
-
- Lee SM, Li ML, Tse YC, Leung SC, Lee MM, Tsui SK, Fung KP, Lee CY, Waye MM. Paeoniae Radix, a Chinese herbal extract, inhibit hepatoma cells growth by inducing apoptosis in a p53 independent pathway. Life Sci. 2002;71:2267–2277. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

