Targeting the epidermal growth factor receptor
- PMID: 15238978
- PMCID: PMC2409851
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6601921
Targeting the epidermal growth factor receptor
Abstract
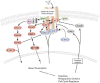
The epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is a member of the erbB family of tyrosine kinase receptors (RTK). The EGFR is involved in cell proliferation, metastasis and angiogenesis, and is expressed in a large proportion of epithelial tumours. The two main classes of EGFR inhibitors in clinical trials are the RTK inhibitors and the monoclonal antibodies. The clinical development of EGFR inhibitors has introduced new challenges to the design of phase I, II, and III trials. Both classes of agents can be safely administered at doses sufficient to inhibit the EGFR system. Receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors have been extensively evaluated in non-small-cell lung cancer. In this setting, gefitinib has demonstrated activity in patients who fail initial chemotherapy. Monoclonal antibodies have been developed in combination with cytotoxic chemotherapy in several tumour types, most notably colorectal and head and neck cancer. The preliminary results suggest an increase in response rate and time to progression with the combination of cetuximab and chemotherapy in both disease models. Future issues in the development of EGFR inhibitors include the identification of biologic predictors of response, combination with other targeted agents, and their utilisation in earlier stage malignancies.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) targeted therapies in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).Rev Recent Clin Trials. 2006 Jan;1(1):1-13. doi: 10.2174/157488706775246157. Rev Recent Clin Trials. 2006. PMID: 18393776 Review.
-
Gefitinib ('Iressa', ZD1839) and new epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors.Br J Cancer. 2004 Feb 9;90(3):566-72. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6601550. Br J Cancer. 2004. PMID: 14760365 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in late stage clinical trials.Expert Opin Emerg Drugs. 2003 Nov;8(2):501-14. doi: 10.1517/14728214.8.2.501. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs. 2003. PMID: 14662002 Review.
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor inhibition strategies in oncology.Endocr Relat Cancer. 2004 Dec;11(4):689-708. doi: 10.1677/erc.1.00600. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2004. PMID: 15613446 Review.
-
Inhibition of the epidermal growth factor receptor in combined modality treatment for locally advanced non-small cell lung cancer.Semin Oncol. 2005 Apr;32(2 Suppl 3):S35-41. doi: 10.1053/j.seminoncol.2005.03.008. Semin Oncol. 2005. PMID: 16015534 Review.
Cited by
-
Therapeutic resistance in cancer: microRNA regulation of EGFR signaling networks.Cancer Biol Med. 2013 Dec;10(4):192-205. doi: 10.7497/j.issn.2095-3941.2013.04.003. Cancer Biol Med. 2013. PMID: 24349829 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A randomized, open-label, two-cycle, two-crossover phase I clinical trial comparing the bioequivalence and safety of afatinib and Giotrif® in healthy Chinese subjects.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023 Jun;149(6):2585-2593. doi: 10.1007/s00432-022-04148-1. Epub 2022 Jun 30. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 35771264 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
EGFR inhibitor enhances cisplatin sensitivity of human glioma cells.J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2011 Dec;31(6):773-778. doi: 10.1007/s11596-011-0675-x. Epub 2011 Dec 16. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2011. PMID: 22173497
-
UBE4B levels are correlated with clinical outcomes in neuroblastoma patients and with altered neuroblastoma cell proliferation and sensitivity to epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors.Cancer. 2013 Feb 15;119(4):915-23. doi: 10.1002/cncr.27785. Epub 2012 Sep 18. Cancer. 2013. PMID: 22990745 Free PMC article.
-
Gefitinib: a review of its use in the management of advanced non-small-cell lung cancer.Drugs. 2004;64(21):2475-92. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200464210-00008. Drugs. 2004. PMID: 15482004 Review.
References
-
- Abbruzzese J, Rosenberg A, Xiong Q, LoBuglio A, Schmidt W, Wolff R, Needle M, Waksal H (2001) Phase II study of anti-epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) antibody cetuximab (IMC-C225) in combination with gemcitabine in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer. Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol 1: 130a - PubMed
-
- Albanell J, Codony-Servat J, Rojo F, Del Campo JM, Sauleda S, Anido J, Raspall G, Giralt J, Rosello J, Nicholson RI, Mendelsohn J, Baselga J (2001) Activated extracellular signal-regulated kinases: association with epidermal growth factor receptor/transforming growth factor alpha expression in head and neck squamous carcinoma and inhibition by anti-epidermal growth factor receptor treatments. Cancer Res 61: 6500–6510 - PubMed
-
- Albanell J, Rojo F, Averbuch S, Feyereislova A, Mascaro JM, Herbst R, LoRusso P, Rischin D, Sauleda S, Gee J, Nicholson RI, Baselga J (2002) Pharmacodynamic studies of the epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor ZD1839 in skin from cancer patients: histopathologic and molecular consequences of receptor inhibition. J Clin Oncol 20: 110–124 - PubMed
-
- Anido J, Matar P, Albanell J, Guzman M, Rojo F, Arribas J, Averbuch S, Baselga J (2003) ZD1839, a specific epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitor, induces the formation of inactive EGFR/HER2 and EGFR/HER3 heterodimers and prevents heregulin signaling in HER2-overexpressing breast cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res 9: 1274–1283 - PubMed
-
- Bailey LR, Kris M, Wolf MK, Kay AC, Averbuch S, Askaa J, Janas M, Schmidt K, Fukuoka M (2003) Tumour EGFR membrane staining is not clinically relevant for predicting response in patients receiving gefitinib montherapy for pretreated non-small cell lung cancer: IDEAL 1 and 2. AACR-NCI-EORTC International Conference. Boston, MA
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous