A ligand-based approach to identify quantitative structure-activity relationships for the androgen receptor
- PMID: 15239655
- PMCID: PMC2080780
- DOI: 10.1021/jm0499007
A ligand-based approach to identify quantitative structure-activity relationships for the androgen receptor
Abstract
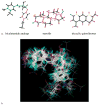
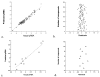
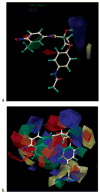
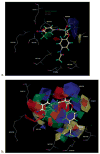
We examined the three-dimensional quantitative structure-activity relationship (QSAR) of a group of endogenous and synthetic compounds for the androgen receptor (AR) using comparative molecular field analysis (CoMFA). The goal of these studies was to identify structural features necessary for high binding affinity and optimization of selective androgen receptor modulators (SARMs). A homology model of the AR was used as a scaffold to align six lead compounds that served as templates for alignment of the remaining 116 structures prior to CoMFA modeling. The conventional r(2) and cross-validated q(2) relating observed and predicted relative binding affinity (RBA) were 0.949 and 0.593, respectively. Comparison of predicted and observed RBA for a test set of 10 compounds resulted in an r(2) of 0.954, demonstrating the excellent predictive ability of the model. These integrated homology modeling and CoMFA studies identified critical amino acids for SARM interactions and provided QSAR data as the basis for mechanistic studies of AR structure, function, and design of optimized SARMs.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Three-dimensional structure-activity relationships of nonsteroidal ligands in complex with androgen receptor ligand-binding domain.J Med Chem. 2005 Feb 24;48(4):917-25. doi: 10.1021/jm0495879. J Med Chem. 2005. PMID: 15715462
-
Key structural features of nonsteroidal ligands for binding and activation of the androgen receptor.Mol Pharmacol. 2003 Jan;63(1):211-23. doi: 10.1124/mol.63.1.211. Mol Pharmacol. 2003. PMID: 12488554
-
Interaction mechanism exploration of R-bicalutamide/S-1 with WT/W741L AR using molecular dynamics simulations.Mol Biosyst. 2015 Dec;11(12):3347-54. doi: 10.1039/c5mb00499c. Epub 2015 Oct 7. Mol Biosyst. 2015. PMID: 26442831
-
Comparative molecular field analysis (CoMFA) model using a large diverse set of natural, synthetic and environmental chemicals for binding to the androgen receptor.SAR QSAR Environ Res. 2003 Oct-Dec;14(5-6):373-88. doi: 10.1080/10629360310001623962. SAR QSAR Environ Res. 2003. PMID: 14758981 Review.
-
Androgen Receptor and Cardiovascular Disease: A Potential Risk for the Abuse of Supplements Containing Selective Androgen Receptor Modulators.Nutrients. 2023 Jul 26;15(15):3330. doi: 10.3390/nu15153330. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37571268 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of nonsteroidal androgen receptor ligands.Pharm Res. 2006 Aug;23(8):1641-58. doi: 10.1007/s11095-006-9024-3. Pharm Res. 2006. PMID: 16841196 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chemistry and structural biology of androgen receptor.Chem Rev. 2005 Sep;105(9):3352-70. doi: 10.1021/cr020456u. Chem Rev. 2005. PMID: 16159155 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Enantioselective γ-C(sp3)-H Activation of Alkyl Amines via Pd(II)/Pd(0) Catalysis.J Am Chem Soc. 2018 Apr 25;140(16):5322-5325. doi: 10.1021/jacs.8b01094. Epub 2018 Apr 11. J Am Chem Soc. 2018. PMID: 29629766 Free PMC article.
-
Structural basis for antagonism and resistance of bicalutamide in prostate cancer.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Apr 26;102(17):6201-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0500381102. Epub 2005 Apr 15. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. PMID: 15833816 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological management of cachexia in adult cancer patients: a systematic review of clinical trials.BMC Cancer. 2018 Nov 27;18(1):1174. doi: 10.1186/s12885-018-5080-4. BMC Cancer. 2018. PMID: 30482179 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dalton JT, et al. Discovery of nonsteroidal androgens. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1998;244(1):1–4. - PubMed
-
- Yin D, et al. Pharmacology, pharmacokinetics, and metabolism of acetothiolutamide, a novel nonsteroidal agonist for the androgen receptor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2003;304(3):1323–1333. - PubMed
-
- Negro-Vilar A. Selective androgen receptor modulators (SARMs): a novel approach to androgen therapy for the new millennium. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1999;84(10):3459–3462. - PubMed
-
- Yin D, et al. Key structural features of nonsteroidal ligands for binding and activation of the androgen receptor. Mol Pharmacol. 2003;63(1):211–223. - PubMed
-
- Yin D, et al. Pharmacodynamics of selective androgen receptor modulators. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2003;304(3):1334–1340. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

