Systematic quantification of gene interactions by phenotypic array analysis
- PMID: 15239834
- PMCID: PMC463315
- DOI: 10.1186/gb-2004-5-7-r49
Systematic quantification of gene interactions by phenotypic array analysis
Abstract
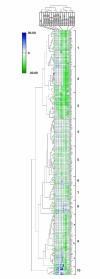
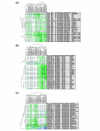
A phenotypic array method, developed for quantifying cell growth, was applied to the haploid and homozygous diploid yeast deletion strain sets. A growth index was developed to screen for non-additive interacting effects between gene deletion and induced perturbations. From a genome screen for hydroxyurea (HU) chemical-genetic interactions, 298 haploid deletion strains were selected for further analysis. The strength of interactions was quantified using a wide range of HU concentrations affecting reference strain growth. The selectivity of interaction was determined by comparison with drugs targeting other cellular processes. Bio-modules were defined as gene clusters with shared strength and selectivity of interaction profiles. The functions and connectivity of modules involved in processes such as DNA repair, protein secretion and metabolic control were inferred from their respective gene composition. The work provides an example of, and a general experimental framework for, quantitative analysis of gene interaction networks that buffer cell growth.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Combined analysis of expression data and transcription factor binding sites in the yeast genome.BMC Genomics. 2004 Aug 26;5(1):59. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-5-59. BMC Genomics. 2004. PMID: 15331021 Free PMC article.
-
Synthetic genetic array (SGA) analysis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Schizosaccharomyces pombe.Methods Enzymol. 2010;470:145-79. doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(10)70007-0. Epub 2010 Mar 1. Methods Enzymol. 2010. PMID: 20946810
-
Comparative analysis of multiple genome-scale data sets.Genome Res. 2002 Oct;12(10):1564-73. doi: 10.1101/gr.225402. Genome Res. 2002. PMID: 12368249 Free PMC article.
-
Toxicogenomics using yeast DNA microarrays.J Biosci Bioeng. 2010 Nov;110(5):511-22. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiosc.2010.06.003. Epub 2010 Jul 10. J Biosci Bioeng. 2010. PMID: 20624688 Review.
-
Chemical-genetic approaches for exploring the mode of action of natural products.Prog Drug Res. 2008;66:237, 239-71. doi: 10.1007/978-3-7643-8595-8_5. Prog Drug Res. 2008. PMID: 18416308 Review.
Cited by
-
Phenomic assessment of genetic buffering by kinetic analysis of cell arrays.Methods Mol Biol. 2014;1205:187-208. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-1363-3_12. Methods Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 25213246 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative analysis of fitness and genetic interactions in yeast on a genome scale.Nat Methods. 2010 Dec;7(12):1017-24. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1534. Epub 2010 Nov 14. Nat Methods. 2010. PMID: 21076421 Free PMC article.
-
Hydroxyurea treatment inhibits proliferation of Cryptococcus neoformans in mice.Front Microbiol. 2012 May 24;3:187. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2012.00187. eCollection 2012. Front Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22783238 Free PMC article.
-
A yeast phenomic model for the gene interaction network modulating CFTR-ΔF508 protein biogenesis.Genome Med. 2012 Dec 27;4(12):103. doi: 10.1186/gm404. Genome Med. 2012. PMID: 23270647 Free PMC article.
-
Accurate, precise modeling of cell proliferation kinetics from time-lapse imaging and automated image analysis of agar yeast culture arrays.BMC Syst Biol. 2007 Jan 8;1:3. doi: 10.1186/1752-0509-1-3. BMC Syst Biol. 2007. PMID: 17408510 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

