SPOC: a widely distributed domain associated with cancer, apoptosis and transcription
- PMID: 15239844
- PMCID: PMC481055
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-5-91
SPOC: a widely distributed domain associated with cancer, apoptosis and transcription
Abstract
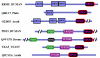
Background: The Split ends (Spen) family are large proteins characterised by N-terminal RNA recognition motifs (RRMs) and a conserved SPOC (Spen paralog and ortholog C-terminal) domain. The aim of this study is to characterize the family at the sequence level.
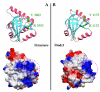
Results: We describe undetected members of the Spen family in other lineages (Plasmodium and Plants) and localise SPOC in a new domain context, in a family that is common to all eukaryotes using profile-based sequence searches and structural prediction methods.
Conclusions: The widely distributed DIO (Death inducer-obliterator) family is related to cancer and apoptosis and offers new clues about SPOC domain functionality.
Figures
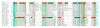
References
-
- Kuang B, Wu SC, Shin Y, Luo L, Kolodziej P. split ends encodes large nuclear proteins that regulate neuronal cell fate and axon extension in the Drosophila embryo. Development. 2000;127:1517–1529. - PubMed
-
- Rebay I, Chen F, Hsiao F, Kolodziej PA, Kuang BH, Laverty T, Suh C, Voas M, Williams A, Rubin GM. A genetic screen for novel components of the Ras/Mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway that interact with the yan gene of Drosophila identifies split ends, a new RNA recognition motif-containing protein. Genetics. 2000;154:695–712. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wiellette EL, Harding KW, Mace KA, Ronshaugen MR, Wang FY, McGinnis W. spen encodes an RNP motif protein that interacts with Hox pathways to repress the development of head-like sclerites in the Drosophila trunk. Development. 1999;126:5373–5385. - PubMed

