Combined immunomagnetic separation-molecular beacon-reverse transcription-PCR assay for detection of hepatitis A virus from environmental samples
- PMID: 15240322
- PMCID: PMC444796
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.70.7.4371-4374.2004
Combined immunomagnetic separation-molecular beacon-reverse transcription-PCR assay for detection of hepatitis A virus from environmental samples
Abstract
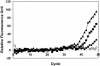
In this study, a molecular-beacon-based real-time reverse transcription (RT)-PCR assay was developed to detect the presence of hepatitis A virus (HAV) in environmental samples. A 125-bp, highly conserved 5' noncoding region of HAV was targeted. The sensitivity of the real-time RT-PCR assay was tested with 10-fold dilutions of viral RNA, and a detection limit of 1 PFU was obtained. The specificity of the assay was demonstrated by testing with other environmental pathogens and indicator microorganisms, and only HAV was positively identified. When combined with immunomagnetic separation, the real-time RT-PCR assay successfully detected as few as 20 PFU in seeded groundwater samples. Because of its simplicity and specificity, this assay has broad applications for the rapid detection of HAV in contaminated foods or water.
Figures

References
-
- Costa-Mattioli, M., S. Monpoeho, E. Nicand, M. H. Aleman, S. Billaudel, and V. Ferré. 2002. Quantification and duration of viraemia during hepatitis A infection as determined by real-time RT-PCR. J. Viral Hepatitis 9:101-106. - PubMed
-
- Grinde, B., T. O. Jonassen, and H. Ushijima. 1995. Sensitive detection of group A rotaviruses by immunomagnetic separation and reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction. J. Virol. Methods 55:327-338. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

