Kinetics and thermodynamics of association of a phospholipid derivative with lipid bilayers in liquid-disordered and liquid-ordered phases
- PMID: 15240470
- PMCID: PMC1304356
- DOI: 10.1529/biophysj.104.040576
Kinetics and thermodynamics of association of a phospholipid derivative with lipid bilayers in liquid-disordered and liquid-ordered phases
Abstract
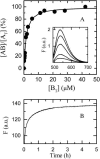
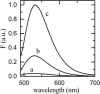
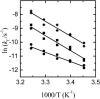
We have measured the rates of insertion into, desorption from, and spontaneous interlayer translocation (flip-flop) in liquid-disordered and liquid-ordered phase lipid bilayer membranes, of the fluorescent phospholipid derivative NBD-dimyristoylphosphatidyl ethanolamine. This study made use of a recently described method that exploits a detailed knowledge of the binding kinetics of an amphiphile to bovine serum albumin, to recover the insertion and desorption rate constants when the albumin-bound amphiphile is transferred through the aqueous phase to the membrane and vice versa. The lipid bilayers, studied as large unilamellar vesicles, were prepared from pure 1-palmitoyl-2-oleoylphosphatidylcholine in the liquid-disordered phase; and from two cholesterol-containing binary lipid mixtures, 1-palmitoyl-2-oleoylphosphatidylcholine and cholesterol (molar ratio of 1:1), and egg sphingomyelin and cholesterol (molar ratio of 6:4), both in the liquid-ordered phase. Insertion, desorption, and translocation rate constants and equilibrium constants for association of the amphiphile monomer with the lipid bilayers were directly measured between 15 degrees and 35 degrees C, and the standard free energies, enthalpies, and entropies, as well as the activation energies for these processes, were derived from this data. The equilibrium partition coefficients for partitioning of the amphiphile between the aqueous phase and the different membrane phases were also derived, and permitted the estimation of hypothetical partition coefficients and the respective energetic parameters for partitioning between the different lipid phases if these were to coexist in the same membrane.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Kinetics and thermodynamics of association of a fluorescent lysophospholipid derivative with lipid bilayers in liquid-ordered and liquid-disordered phases.Biophys J. 2005 Jun;88(6):4064-71. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.104.054007. Epub 2005 Mar 25. Biophys J. 2005. PMID: 15792982 Free PMC article.
-
Binding of a fluorescent lipid amphiphile to albumin and its transfer to lipid bilayer membranes.Biophys J. 2003 Jan;84(1):386-99. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(03)74859-0. Biophys J. 2003. PMID: 12524292 Free PMC article.
-
Kinetics and thermodynamics of the association of dehydroergosterol with lipid bilayer membranes.Biophys J. 2007 Dec 15;93(12):4244-53. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.107.112847. Epub 2007 Aug 31. Biophys J. 2007. PMID: 17766353 Free PMC article.
-
Thermodynamics of lipid interactions in complex bilayers.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009 Jan;1788(1):72-85. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2008.08.007. Epub 2008 Aug 15. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009. PMID: 18775410 Review.
-
Complex biomembrane mimetics on the sub-nanometer scale.Biophys Rev. 2017 Aug;9(4):353-373. doi: 10.1007/s12551-017-0275-5. Epub 2017 Jul 17. Biophys Rev. 2017. PMID: 28717925 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Lipid vesicles chaperone an encapsulated RNA aptamer.Nat Commun. 2018 Jun 13;9(1):2313. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-04783-8. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 29899431 Free PMC article.
-
Spontaneous, intervesicular transfer rates of fluorescent, acyl chain-labeled phosphatidylcholine analogs.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007 Mar;1768(3):502-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2006.11.013. Epub 2006 Dec 5. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007. PMID: 17198675 Free PMC article.
-
Kinetics and thermodynamics of lipid amphiphile exchange between lipoproteins and albumin in serum.Biophys J. 2005 Jan;88(1):557-65. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.104.047050. Epub 2004 Oct 1. Biophys J. 2005. PMID: 15465860 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Acyl Chain Length on the Rate of Phospholipid Flip-Flop and Intermembrane Transfer.J Membr Biol. 2018 Jun;251(3):431-442. doi: 10.1007/s00232-017-0009-4. Epub 2017 Dec 20. J Membr Biol. 2018. PMID: 29264685
-
Cholesterol slows down the lateral mobility of an oxidized phospholipid in a supported lipid bilayer.Langmuir. 2010 Nov 16;26(22):17322-9. doi: 10.1021/la1026202. Epub 2010 Oct 13. Langmuir. 2010. PMID: 20942393 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aniansson, E. A. G., S. N. Wall, M. Almgren, H. Hoffmann, I. Klelmann, W. Ulbricht, R. Zana, J. Lang, and C. Tondre. 1976. Theory of the kinetics of micellar equilibria and quantitative interpretation of chemical relaxation studies of micellar solutions of ionic surfactants. J. Phys. Chem. 80:905–922.
-
- Bartlett, G. R. 1959. Phosphorous assay in column chromatography. J. Biol. Chem. 234:466–468. - PubMed
-
- Brown, D. A., and E. London. 1998. Functions of lipid rafts in biological membranes. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 14:111–136. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

