Arabidopsis CYP86A2 represses Pseudomonas syringae type III genes and is required for cuticle development
- PMID: 15241470
- PMCID: PMC514950
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600290
Arabidopsis CYP86A2 represses Pseudomonas syringae type III genes and is required for cuticle development
Abstract
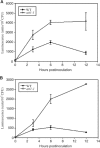
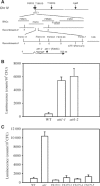
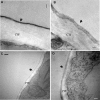
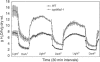
Pseudomonas syringae relies on type III secretion system to deliver effector proteins into the host cell for parasitism. Type III genes are induced in planta, but host factors affecting the induction are poorly understood. Here we report on the identification of an Arabidopsis mutant, att1 (for aberrant induction of type three genes), that greatly enhances the expression of bacterial type III genes avrPto and hrpL. att1 plants display enhanced disease severity to a virulent strain of P. syringae, suggesting a role of ATT1 in disease resistance. ATT1 encodes CYP86A2, a cytochrome P450 monooxygenase catalyzing fatty acid oxidation. The cutin content is reduced to 30% in att1, indicating that CYP86A2 plays a major role in the biosynthesis of extracellular lipids. att1 has a loose cuticle membrane ultrastructure and shows increased permeability to water vapor, demonstrating the importance of the cuticle membrane in controlling water loss. The enhanced avrPto-luc expression is specific to att1, but not another cuticle mutant, wax2. The results suggest that certain cutin-related fatty acids synthesized by CYP86A2 may repress bacterial type III gene expression in the intercellular spaces.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Mutations in LACS2, a long-chain acyl-coenzyme A synthetase, enhance susceptibility to avirulent Pseudomonas syringae but confer resistance to Botrytis cinerea in Arabidopsis.Plant Physiol. 2007 Jun;144(2):1093-103. doi: 10.1104/pp.106.094318. Epub 2007 Apr 13. Plant Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17434992 Free PMC article.
-
A DeoR-Type Transcription Regulator Is Required for Sugar-Induced Expression of Type III Secretion-Encoding Genes in Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato DC3000.Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2020 Mar;33(3):509-518. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-10-19-0290-R. Epub 2020 Jan 23. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2020. PMID: 31829102
-
The Erwinia amylovora avrRpt2EA gene contributes to virulence on pear and AvrRpt2EA is recognized by Arabidopsis RPS2 when expressed in pseudomonas syringae.Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2006 Jun;19(6):644-54. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-19-0644. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2006. PMID: 16776298
-
Activation of a COI1-dependent pathway in Arabidopsis by Pseudomonas syringae type III effectors and coronatine.Plant J. 2004 Feb;37(4):589-602. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313x.2003.01986.x. Plant J. 2004. PMID: 14756769
-
Arabidopsis PAD3, a gene required for camalexin biosynthesis, encodes a putative cytochrome P450 monooxygenase.Plant Cell. 1999 Dec;11(12):2419-28. doi: 10.1105/tpc.11.12.2419. Plant Cell. 1999. PMID: 10590168 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
An eceriferum locus, cer-zv, is associated with a defect in cutin responsible for water retention in barley (Hordeum vulgare) leaves.Theor Appl Genet. 2013 Mar;126(3):637-46. doi: 10.1007/s00122-012-2007-3. Epub 2012 Nov 4. Theor Appl Genet. 2013. PMID: 23124432
-
A radioactive assay allowing the quantitative measurement of cuticular permeability of intact Arabidopsis thaliana leaves.Planta. 2011 Jul;234(1):9-20. doi: 10.1007/s00425-011-1381-4. Epub 2011 Feb 23. Planta. 2011. PMID: 21344313
-
Combining Physio-Biochemical Characterization and Transcriptome Analysis Reveal the Responses to Varying Degrees of Drought Stress in Brassica napus L.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 2;23(15):8555. doi: 10.3390/ijms23158555. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35955689 Free PMC article.
-
An extensive (co-)expression analysis tool for the cytochrome P450 superfamily in Arabidopsis thaliana.BMC Plant Biol. 2008 Apr 23;8:47. doi: 10.1186/1471-2229-8-47. BMC Plant Biol. 2008. PMID: 18433503 Free PMC article.
-
Cutinsomes and lipotubuloids appear to participate in cuticle formation in Ornithogalum umbellatum ovary epidermis: EM-immunogold research.Protoplasma. 2014 Sep;251(5):1151-61. doi: 10.1007/s00709-014-0623-2. Epub 2014 Mar 14. Protoplasma. 2014. PMID: 24627134 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arlat M, Gough CL, Zischek C, Barberis PA, Trigalet A, Boucher CA (1992) Transcriptional organization and expression of the large hrp gene cluster of Pseudomonas solanacearum. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 5: 187–193 - PubMed
-
- Beneviste I, Tijet N, Adas F, Philipps G, Salaun JP, Durst F (1998) CYP86A1 from Arabidopsis thaliana encodes a cytochrome P450-dependent fatty acid omega-hydroxylase. Biochem Biophys Res Commmun 243: 688–693 - PubMed
-
- Brito B, Aldon D, Barberis P, Boucher C, Genin S (2002) A signal transfer system through three compartments transduces the plant cell contact-dependent signal controlling Ralstonia solanacearum hrp genes. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 15: 109–119 - PubMed
-
- Brito B, Marenda M, Barberis P, Boucher C, Genin S (1999) prhJ and hrpG, two new components of the plant signal-dependent regulatory cascade controlled by PrhA in Ralstonia solanacearum. Mol Microbiol 31: 237–251 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

