A class of plant glycosyltransferases involved in cellular homeostasis
- PMID: 15241472
- PMCID: PMC514916
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600295
A class of plant glycosyltransferases involved in cellular homeostasis
Abstract
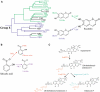
Many small lipophilic compounds in living cells can be modified by glycosylation. These processes can regulate the bioactivity of the compounds, their intracellular location and their metabolism. The glycosyltransferases involved in biotransformations of small molecules have been grouped into Family 1 of the 69 families that are classified on the basis of substrate recognition and sequence relatedness. In plants, these transfer reactions generally use UDP-glucose with acceptors that include hormones such as auxins and cytokinins, secondary metabolites such as flavonoids, and foreign compounds including herbicides and pesticides. In mammalian organisms, UDP-glucuronic acid is typically used in the transfer reactions to endogenous acceptors, such as steroid and thyroid hormones, bile acids and retinoids, and to xenobiotics, including nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and dietary metabolites. There is widespread interest in this class of enzyme since they are known to function both in the regulation of cellular homeostasis and in detoxification pathways. This review outlines current knowledge of these glycosyltransferases drawing on information gained from studies of plant and mammalian enzymes.
Figures


References
-
- Aherne SA, O'Brien NM (2002) Dietary flavonols: chemistry, food content, and metabolism. Nutrition 18: 75–81 - PubMed
-
- Arend J, Warzecha H, Hefner T, Stockigt J (2001) Utilizing genetically engineered bacteria to produce plant-specific glucosides. Biotechnol Bioeng 76: 126–131 - PubMed
-
- Bock KW (2003) Vertebrate UDP-glucuronosyltransferases: functional and evolutionary aspects. Biochem Pharmacol 66: 691–696 - PubMed
-
- Bosio A, Binczek E, Lebeau MM, Fernald AA, Stoffel W (1996) The human gene CGT encoding the UDP-galactose ceramide galactosyl transferase (cerebroside synthase): cloning, characterization, and assignment to human chromosome 4, band q26. Genomics 34: 69–75 - PubMed
-
- Bouktaib M, Atmani A, Rolando C (2002) Regio- and stereoselective synthesis of the major metabolite of quercetin, quercetin-3-O-β-D-glucuronide. Tetrahedron Lett 43: 6263–6266
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

