GRK2 is an endogenous protein inhibitor of the insulin signaling pathway for glucose transport stimulation
- PMID: 15241473
- PMCID: PMC514955
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600297
GRK2 is an endogenous protein inhibitor of the insulin signaling pathway for glucose transport stimulation
Abstract
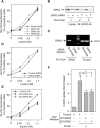
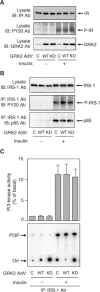
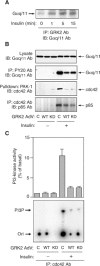
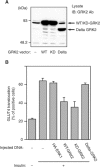
G protein-coupled receptor kinases (GRKs) represent a class of proteins that classically phosphorylate agonist-activated G protein-coupled receptors, leading to uncoupling of the receptor from further G protein activation. Recently, we have reported that the heterotrimeric G protein alpha-subunit, Galphaq/11, can mediate insulin-stimulated glucose transport. GRK2 contains a regulator of G protein signaling (RGS) domain with specificity for Galphaq/11. Therefore, we postulated that GRK2 could be an inhibitor of the insulin signaling cascade leading to glucose transport in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. In this study, we demonstrate that microinjection of anti-GRK2 antibody or siRNA against GRK2 increased insulin-stimulated insulin-responsive glucose transporter 4 (GLUT4) translocation, while adenovirus-mediated overexpression of wild-type or kinase-deficient GRK2 inhibited insulin-stimulated GLUT4 translocation as well as 2-deoxyglucose uptake. Importantly, a mutant GRK2 lacking the RGS domain was without effect. Taken together, these results indicate that through its RGS domain endogenous GRK2 functions as a negative regulator of insulin-stimulated glucose transport by interfering with Galphaq/11 signaling to GLUT4 translocation. Furthermore, inhibitors of GRK2 can lead to enhanced insulin sensitivity.
Figures
Similar articles
-
G protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 mediates endothelin-1-induced insulin resistance via the inhibition of both Galphaq/11 and insulin receptor substrate-1 pathways in 3T3-L1 adipocytes.Mol Endocrinol. 2005 Nov;19(11):2760-8. doi: 10.1210/me.2004-0429. Epub 2005 Jun 30. Mol Endocrinol. 2005. PMID: 15994203
-
G alpha-q/11 protein plays a key role in insulin-induced glucose transport in 3T3-L1 adipocytes.Mol Cell Biol. 1999 Oct;19(10):6765-74. doi: 10.1128/MCB.19.10.6765. Mol Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 10490615 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic endothelin-1 treatment leads to heterologous desensitization of insulin signaling in 3T3-L1 adipocytes.J Clin Invest. 2001 May;107(9):1193-202. doi: 10.1172/JCI11753. J Clin Invest. 2001. PMID: 11342583 Free PMC article.
-
[Regulation of insulin sensitivity by subcellular GLUT4 targeting].Rinsho Byori. 2005 Oct;53(10):942-9. Rinsho Byori. 2005. PMID: 16296343 Review. Japanese.
-
Insulin signaling in microdomains of the plasma membrane.Traffic. 2003 Nov;4(11):711-6. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0854.2003.00119.x. Traffic. 2003. PMID: 14617354 Review.
Cited by
-
Trafficking GRK2: Cellular and Metabolic consequences of GRK2 subcellular localization.Transl Med UniSa. 2014 Apr 8;10:3-7. eCollection 2014 Sep. Transl Med UniSa. 2014. PMID: 25147759 Free PMC article. Review.
-
G protein-coupled receptor kinases as regulators of dopamine receptor functions.Pharmacol Res. 2016 Sep;111:1-16. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2016.05.010. Epub 2016 May 10. Pharmacol Res. 2016. PMID: 27178731 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antidiabetic and Cardioprotective Effects of Pharmacological Inhibition of GRK2 in db/db Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Mar 25;20(6):1492. doi: 10.3390/ijms20061492. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30934608 Free PMC article.
-
G protein-coupled receptor kinase 2: a link between myocardial contractile function and cardiac metabolism.Circ Res. 2014 May 9;114(10):1661-70. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.114.300513. Circ Res. 2014. PMID: 24812353 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Metabolic Role of GRK2 in Insulin Resistance and Associated Conditions.Cells. 2021 Jan 15;10(1):167. doi: 10.3390/cells10010167. Cells. 2021. PMID: 33467677 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Baltensperger K, Karoor V, Paul H, Ruoho A, Czech MP, Malbon CC (1996) The beta-adrenergic receptor is a substrate for the insulin receptor tyrosine kinase. J Biol Chem 271: 1061–1064 - PubMed
-
- Carman CV, Parent JL, Day PW, Pronin AN, Sternweis PM, Wedegaertner PB, Gilman AG, Benovic JL, Kozasa T (1999) Selective regulation of Galpha(q/11) by an RGS domain in the G protein-coupled receptor kinase, GRK2. J Biol Chem 274: 34483–34492 - PubMed
-
- Chen JF, Guo JH, Moxham CM, Wang HY, Malbon CC (1997) Conditional, tissue-specific expression of Q205L G alpha i2 in vivo mimics insulin action. J Mol Med 75: 283–289 - PubMed
-
- Dalle S, Ricketts W, Imamura T, Vollenweider P, Olefsky JM (2001) Insulin and insulin-like growth factor I receptors utilize different G protein signaling components. J Biol Chem 276: 15688–15695 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

