Tumor suppressor IRF-1 mediates retinoid and interferon anticancer signaling to death ligand TRAIL
- PMID: 15241475
- PMCID: PMC514919
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600302
Tumor suppressor IRF-1 mediates retinoid and interferon anticancer signaling to death ligand TRAIL
Abstract
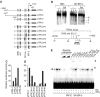
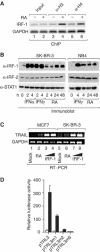
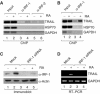
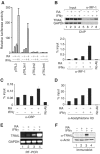
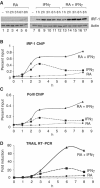
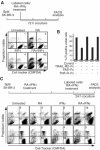
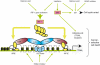
Retinoids and interferons are signaling molecules with pronounced anticancer activity. We show that in both acute promyelocytic leukemia and breast cancer cells the retinoic acid (RA) and interferon signaling pathways converge on the promoter of the tumoricidal death ligand TRAIL. Promoter mapping, chromatin immunoprecipitation and RNA interference reveal that retinoid-induced interferon regulatory factor-1 (IRF-1), a tumor suppressor, is critically required for TRAIL induction by both RA and IFNgamma. Exposure of breast cancer cells to both antitumor agents results in enhanced TRAIL promoter occupancy by IRF-1 and coactivator recruitment, leading to strong histone acetylation and synergistic induction of TRAIL expression. In coculture experiments, pre-exposure of breast cancer cells to RA and IFNgamma induced a dramatic TRAIL-dependent apoptosis in heterologous cancer cells in a paracrine mode of action, while normal cells were not affected. Our results identify a novel TRAIL-mediated tumor suppressor activity of IRF-1 and suggest a mechanistic basis for the synergistic antitumor activities of certain retinoids and interferons. These data argue for combination therapies that activate the TRAIL pathway to eradicate tumor cells.
Figures
Similar articles
-
IFN-gamma enhances TRAIL-induced apoptosis through IRF-1.Eur J Biochem. 2004 Nov;271(21):4222-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.2004.04362.x. Eur J Biochem. 2004. PMID: 15511228
-
Co-resistance to retinoic acid and TRAIL by insertion mutagenesis into RAM.Oncogene. 2006 Jun 22;25(26):3735-44. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1209410. Epub 2006 Jan 30. Oncogene. 2006. PMID: 16449964
-
Physiological and receptor-selective retinoids modulate interferon gamma signaling by increasing the expression, nuclear localization, and functional activity of interferon regulatory factor-1.J Biol Chem. 2005 Oct 28;280(43):36228-36. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M505749200. Epub 2005 Aug 5. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 16085646 Free PMC article.
-
Interferon-gamma and TRAIL in human breast tumor cells.Vitam Horm. 2004;67:291-318. doi: 10.1016/S0083-6729(04)67016-6. Vitam Horm. 2004. PMID: 15110183 Review.
-
Retinoic-acid-induced apoptosis in leukemia cells.Trends Mol Med. 2004 Oct;10(10):508-15. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2004.08.006. Trends Mol Med. 2004. PMID: 15464451 Review.
Cited by
-
Roles of Interferon Regulatory Factor 1 in Tumor Progression and Regression: Two Sides of a Coin.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 10;25(4):2153. doi: 10.3390/ijms25042153. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38396830 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Arsenic trioxide-mediated growth inhibition of myeloma cells is associated with an extrinsic or intrinsic signaling pathway through activation of TRAIL or TRAIL receptor 2.Cancer Biol Ther. 2010 Dec 1;10(11):1201-14. doi: 10.4161/cbt.10.11.13669. Epub 2010 Dec 1. Cancer Biol Ther. 2010. PMID: 20953137 Free PMC article.
-
Arsenic trioxide and sorafenib combination therapy for human hepatocellular carcinoma functions via up-regulation of TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand.Oncol Lett. 2018 Sep;16(3):3341-3350. doi: 10.3892/ol.2018.8981. Epub 2018 Jun 18. Oncol Lett. 2018. PMID: 30127933 Free PMC article.
-
IL-27 enhances the expression of TRAIL and TLR3 in human melanomas and inhibits their tumor growth in cooperation with a TLR3 agonist poly(I:C) partly in a TRAIL-dependent manner.PLoS One. 2013 Oct 14;8(10):e76159. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0076159. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24155891 Free PMC article.
-
The synergistic interaction between the calcineurin B subunit and IFN-γ enhances macrophage antitumor activity.Cell Death Dis. 2015 May 7;6(5):e1740. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2015.92. Cell Death Dis. 2015. PMID: 25950470 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alcalay M, Meani N, Gelmetti V, Fantozzi A, Fagioli M, Orleth A, Riganelli D, Sebastiani C, Cappelli E, Casciari C, Sciurpi MT, Mariano AR, Minardi SP, Luzi L, Muller H, Di Fiore PP, Frosina G, Pelicci PG (2003) Acute myeloid leukemia fusion proteins deregulate genes involved in stem cell maintenance and DNA repair. J Clin Invest 112: 1751–1761 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Almasan A, Ashkenazi A (2003) Apo2L/TRAIL: apoptosis signaling, biology, and potential for cancer therapy. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 14: 337–348 - PubMed
-
- Altucci L, Gronemeyer H (2001) The promise of retinoids to fight against cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 1: 181–193 - PubMed
-
- Altucci L, Gronemeyer H (2004) Retinoids and TRAIL: two cooperating actors to fight against cancer. In Vitamins and Hormones, Litwack G (ed) Vol. 67, pp 319–345. Academic Press: Elsevier - PubMed
-
- Altucci L, Rossin A, Raffelsberger W, Reitmair A, Chomienne C, Gronemeyer H (2001) Retinoic acid-induced apoptosis in leukemia cells is mediated by paracrine action of tumor-selective death ligand TRAIL. Nat Med 7: 680–686 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

