Neck pain and disability following motor vehicle accidents--a cohort study
- PMID: 15241671
- PMCID: PMC3476670
- DOI: 10.1007/s00586-004-0766-5
Neck pain and disability following motor vehicle accidents--a cohort study
Abstract
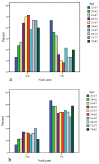
The primary aim of the study was to compare the prevalence of neck pain and disability in a group exposed to motor vehicle accidents (MVAs) with those in the general population. The secondary aim was to assess the prevalence of a past history of exposure to an MVA with sequelae of neck pain in the general population. The exposed group consisted of 121 patients with neck complaints following an MVA in 1983. The control group, consisting of 1,491 subjects, was randomly selected, with attention to the distribution of age and gender in the exposed group. A neck-pain questionnaire was mailed to the subjects. In the control group, it included enquiry about a history of exposure to an MVA with sequelae of neck pain. The Neck Disability Index (NDI) was used to assess neck-related disability. In the exposed group 108 subjects (89%) responded, and in the control group 931 (62%) did. Seventeen years after the MVA, 59 subjects (55%) reported neck pain in the exposed group, with no gender differences. In the control group 270 (29%) reported neck pain with a higher frequency among women (34%) than men (19%) (p<0.01). There was a significant difference between the exposed group and the control group regarding the occurrence of neck pain (p<0.001). In the control group 34% recalled a history of an MVA, among whom one-third reported neck pain in connection with the accident and 28% had persistent neck pain referable to the accident. The exposed group scored significantly higher on the NDI (p<0.001) and reported significantly higher neck pain intensity than did the control group (p<0.001). In conclusion, a past history of exposure to an MVA with sequelae of neck pain appears to have a substantial impact on future persistent neck pain and associated disability.
Figures
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous