Allergenic characterization of tropomyosin from the dusky brown cockroach, Periplaneta fuliginosa
- PMID: 15242941
- PMCID: PMC440615
- DOI: 10.1128/CDLI.11.4.680-685.2004
Allergenic characterization of tropomyosin from the dusky brown cockroach, Periplaneta fuliginosa
Erratum in
- Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 2006 May;13(5):602
Abstract
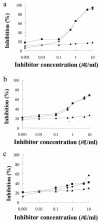
Household arthropods are one of the most common causes of allergic diseases. Four species of cockroaches are found to reside in Korean homes, but published work deals almost exclusively with the German and American cockroaches. This study was undertaken to investigate the cross-reactive allergenic components of the dusky brown cockroach, Periplaneta fuliginosa. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) inhibition and immunoblot analyses for the dusky brown cockroach were performed with Blattella germanica and Dermatophagoides farinae allergic sera. cDNA encoding tropomyosin, which is a well known cross-reactive pan-allergen, was cloned by reverse transcriptase PCR, and recombinant protein was produced by using a pET-28b expression system. Native tropomyosin was purified by ammonium sulfate fractionation and electroelution. The immunoglobulin E (IgE) reactivities of native and recombinant tropomyosins were compared by an ELISA inhibition study. All 30 sera tested showed P. fuliginosa-specific IgE, and the IgE-binding reactivity of the P. fuliginosa extract was inhibited as much as 79.4% by a B. germanica extract and as much as 63.3% by a D. farinae extract. The deduced amino acid sequence of cloned cDNA was identical with that of Periplaneta americana tropomyosin (98.5% nucleotide sequence identity). Seven of 26 (26.9%) allergic sera had IgE specific for recombinant protein, and the maximum inhibition of P. fuliginosa-specific IgE achieved with recombinant tropomyosin was 37.7% at an inhibitor concentration of 10 microg/ml. Native tropomyosin inhibited the binding of IgE to the P. fuliginosa, B. germanica, and D. farinae extracts by 65.0, 51.8, and 39% at an inhibitor concentration of 1 microg/ml. P. fuliginosa appears to possess allergens that are highly cross-reactive with allergens of B. germanica and D. farinae. Tropomyosin was found to be a major allergenic component accounting for the cross-reactivity between cockroaches and dust mites.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Molecular characterization of American cockroach tropomyosin (Periplaneta americana allergen 7), a cross-reactive allergen.J Immunol. 1999 Apr 1;162(7):4342-8. J Immunol. 1999. PMID: 10201967
-
[The specific IgE responses to three cockroach strains antigens in patients with asthma].Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi. 2006 Jul;45(7):556-8. Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi. 2006. PMID: 17074109 Chinese.
-
Expression of tropomyosin from Blattella germanica as a recombinant non-fusion protein in Pichia pastoris and comparison of its IgE reactivity with its native counterpart.Protein Expr Purif. 2004 Oct;37(2):273-8. doi: 10.1016/j.pep.2004.06.009. Protein Expr Purif. 2004. PMID: 15358347
-
Tropomyosin: an invertebrate pan-allergen.Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 1999 Aug;119(4):247-58. doi: 10.1159/000024201. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 1999. PMID: 10474029 Review.
-
Allergenic tropomyosins and their cross-reactivities.Protein Pept Lett. 2006;13(8):835-45. doi: 10.2174/092986606777841244. Protein Pept Lett. 2006. PMID: 17073731 Review.
Cited by
-
Cross-reactivity and sensitization profiles of cockroach and moth allergens provide new insights in cockroach-allergic patients.World Allergy Organ J. 2025 May 7;18(5):101057. doi: 10.1016/j.waojou.2025.101057. eCollection 2025 May. World Allergy Organ J. 2025. PMID: 40469215 Free PMC article.
-
Investigating cockroach allergens: aiming to improve diagnosis and treatment of cockroach allergic patients.Methods. 2014 Mar 1;66(1):75-85. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2013.07.036. Epub 2013 Aug 2. Methods. 2014. PMID: 23916425 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Detecting Allergens From Black Tiger Shrimp Penaeus monodon That Can Bind and Cross-link IgE by ELISA, Western Blot, and a Humanized Rat Basophilic Leukemia Reporter Cell Line RS-ATL8.Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2018 Jan;10(1):62-76. doi: 10.4168/aair.2018.10.1.62. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2018. PMID: 29178679 Free PMC article.
-
A cross-sectional observational study on allergen-specific IgE positivity in a southeast coastal versus a southwest inland region of China.Sci Rep. 2017 Aug 30;7(1):9593. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-10109-3. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28855606 Free PMC article.
-
Household arthropod allergens in Korea.Korean J Parasitol. 2009 Oct;47 Suppl(Suppl):S143-53. doi: 10.3347/kjp.2009.47.S.S143. Korean J Parasitol. 2009. PMID: 19885330 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aalberse, R. C., J. H. Akkerdaas, and R. van Ree. 2001. Cross-reactivity of IgE antibodies to allergens. Allergy 56:478-490. - PubMed
-
- Aki, T., T. Kodama, A. Fugikawa, K. Miura, S. Shigeta, T. Wada, T. Jyo, Y. Murooka, S. Oka, and K. Ono. 1995. Immunochemical characterization of recombinant and native tropomyosin as a new allergen from the house dust mite, Dermatophagoides farinae. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 96:74-83. - PubMed
-
- Appel, A. G., and L. M. Smith II. 2002. Biology and management of the smokybrown cockroach. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 47:33-55. - PubMed
-
- Arruda, L. K., L. D. Vailes, B. J. Mann, J. Shannon, J. W. Fox, and T. S. Vedvick. 1995. Molecular cloning of a major cockroach (Blattella germanica) allergen, Bla g 2. Sequence homology to the aspartic proteases. J. Biol. Chem. 270:19563-19568. - PubMed
-
- Arruda, L. K., L. D. Vailes, M. L. Hayden, D. C. Benjamin, and M. D. Chapman. 1995. Cloning of cockroach allergen, Bla g 4, identifies ligand binding proteins (or calycins) as a cause of IgE antibody responses. J. Biol. Chem. 270:31196-31201. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

