Differential proteomic analysis of human hepatocellular carcinoma cell line metastasis-associated proteins
- PMID: 15243804
- PMCID: PMC12161779
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-004-0576-5
Differential proteomic analysis of human hepatocellular carcinoma cell line metastasis-associated proteins
Abstract
Purpose: The comparative study of differentially expression of protein profiles of hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines with various metastasic potential and screening key molecules related to hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis and recurrence.
Methods: Using two-dimensional electrophoresis and liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-ESI-MS/MS), we analyzed differentially displayed proteomics of human hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines Hep3B, MHCC97L, MHCC97H with different metastasic potential.
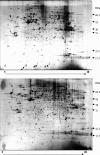
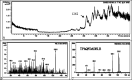
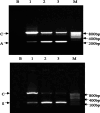
Results: Approximate 1,000 protein spots were detected on silver-stained gel by ImageMaster (977+/-113 spots in Hep3B, 1092+/-40 in MHCC97L, and 889+/-14 in MHCC97H). Fifty distinct different protein spots were analyzed with online LC-ESI-MS/MS. Only 26 protein spots had a positive result, including annexin1, S100A4, and so on. In comparison with nonmetastasis Hep3B cell lines, there were 16 proteins overexpressed in MHCC97H and MHCC97L, 10 proteins underexpressed in MHCC97H and MHCC97L. Applying cell immunohistochemistry and RT-PCR, we further validated two interesting and different proteins, annexin1 and S100A4.
Conclusion: The protein profile of metastatic hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines displayed obvious differences compared with non-metastatic liver cancer cell lines. The results imply that various different proteins may lead to HCC metastasis together.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Proteomic analysis on metastasis-associated proteins of human hepatocellular carcinoma tissues.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2006 Feb;132(2):92-8. doi: 10.1007/s00432-005-0044-x. Epub 2005 Nov 1. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2006. PMID: 16261346 Free PMC article.
-
A decade's studies on metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2004 Apr;130(4):187-96. doi: 10.1007/s00432-003-0511-1. Epub 2003 Dec 18. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2004. PMID: 14685850 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Differential proteomic analysis of a highly metastatic variant of human breast cancer cells using two-dimensional differential gel electrophoresis.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2010 Oct;136(10):1545-56. doi: 10.1007/s00432-010-0812-0. Epub 2010 Feb 14. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2010. PMID: 20155427 Free PMC article.
-
Differential proteomic analysis of human colorectal carcinoma cell lines metastasis-associated proteins.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2007 Oct;133(10):771-82. doi: 10.1007/s00432-007-0222-0. Epub 2007 May 15. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2007. PMID: 17503081 Free PMC article.
-
Ablative and non-surgical therapies for early and very early hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review and network meta-analysis.Health Technol Assess. 2023 Dec;27(29):1-172. doi: 10.3310/GK5221. Health Technol Assess. 2023. PMID: 38149643 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
A Quest for New Cancer Diagnosis, Prognosis and Prediction Biomarkers and Their Use in Biosensors Development.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2020 Jan-Dec;19:1533033820957033. doi: 10.1177/1533033820957033. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2020. PMID: 33107395 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In silico Prediction of Deleterious Single Nucleotide Polymorphism in S100A4 Metastatic Gene: Potential Early Diagnostic Marker.Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2022 Jul 31;2022:4202623. doi: 10.1155/2022/4202623. eCollection 2022. Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2022. PMID: 35965620 Free PMC article.
-
Application of proteomics in the study of tumor metastasis.Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2004 Aug;2(3):152-66. doi: 10.1016/s1672-0229(04)02021-2. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2004. PMID: 15862116 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proteomic analysis on metastasis-associated proteins of human hepatocellular carcinoma tissues.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2006 Feb;132(2):92-8. doi: 10.1007/s00432-005-0044-x. Epub 2005 Nov 1. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2006. PMID: 16261346 Free PMC article.
-
The metastasis associated protein S100A4: role in tumour progression and metastasis.Br J Cancer. 2005 Jun 6;92(11):1955-8. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6602613. Br J Cancer. 2005. PMID: 15900299 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Brunagel G, Schoen RE, Bauer AJ, Vietmeier BN, Getzenberg RH (2002) Nuclear matrix protein alterations associated with colon cancer metastasis to the liver. Clin Cancer Res 8:3039–3045 - PubMed
-
- Coffey DS(2002) Nuclear matrix proteins as proteomic marks of preneoplastic and cancer lesions. Clin Cancer Res 8:3031–3033 - PubMed
-
- Hanazaki K, Kajikawa S, Shimozawa N, Mihara M, Shimada K, Hiraguri M, Koide N, Adachi W, Amano J (2000) Survival and recurrence after hepatic resection of 386 consecutive patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. J Am Coll Surg 191:381–388 - PubMed
-
- Komatsu K, Kobune-Fujiwara Y, Andoh A, Ishiguro S, Hunai H, Suzuki N, Kameyama M, Murata K, Miyoshi J, Akedo H, Tatsuta M, Nakamura H (2000) Increased expression of S100A6 at the invading fronts of the primary lesion and liver metastasis in patients with colorectal adenocarcinoma. Br J Cancer 83:769–774 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

