Altered visceral perceptual and neuroendocrine response in patients with irritable bowel syndrome during mental stress
- PMID: 15247175
- PMCID: PMC1774150
- DOI: 10.1136/gut.2003.017962
Altered visceral perceptual and neuroendocrine response in patients with irritable bowel syndrome during mental stress
Abstract
Background and aims: Stress often worsens the symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). We hypothesised that this might be explained by altered neuroendocrine and visceral sensory responses to stress in IBS patients.
Subjects and methods: Eighteen IBS patients and 22 control subjects were assessed using rectal balloon distensions before, during, and after mental stress. Ten controls and nine patients were studied in supplementary sessions. Rectal sensitivity (thresholds and intensity-visual analogue scale (VAS)) and perceived stress and arousal (VAS) were determined. Plasma levels of corticotropin releasing factor (CRF), adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), cortisol, noradrenaline, and adrenaline were analysed at baseline, immediately after stress, and after the last distension. Heart rate was recorded continuously.
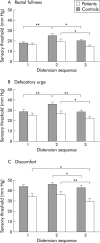
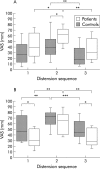
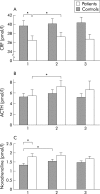
Results: Thresholds were increased during stress in control subjects (p<0.01) but not in IBS patients. Both groups showed lower thresholds after stress (p<0.05). Repeated distensions without stress did not affect thresholds. Both groups showed increased heart rate (p<0.001) and VAS ratings for stress and arousal (p<0.05) during stress. Patients demonstrated higher ratings for stress but lower for arousal than controls. Basal CRF levels were lower in patients (p<0.05) and increased significantly during stress in patients (p<0.01) but not in controls. Patients also responded with higher levels of ACTH during stress (p<0.05) and had higher basal levels of noradrenaline than controls (p<0.01). Controls, but not patients, showed increased levels of adrenaline and noradrenaline in response to stress (p<0.05).
Conclusions: Stress induced exaggeration of the neuroendocrine response and visceral perceptual alterations during and after stress may explain some of the stress related gastrointestinal symptoms in IBS.
Figures

References
-
- Agreus L , Svärdsudd K, Nyren O, et al. Irritable bowel syndrome and dyspepsia in the general population: overlap and lack of stability over time. Gastroenterology 1995;109:671–80. - PubMed
-
- Fukudo S , Suzuki J. Colonic motility, autonomic function, and gastrointestinal hormones under psychological stress on irritable bowel syndrome. Tohoku J Exp Med 1987;151:373–85. - PubMed
-
- Welgan P , Meshkinpour H, Beeler M. Effect of anger on colon motor and myoelectric activity in irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology 1988;94 (Pt 1) :1150–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
