APE1 is the major 3'-phosphoglycolate activity in human cell extracts
- PMID: 15247342
- PMCID: PMC484167
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkh676
APE1 is the major 3'-phosphoglycolate activity in human cell extracts
Abstract
DNA strand breaks containing 3'-phosphoglycolate (3'-PG) ends are the major lesions induced by ionizing radiation. The repair of this lesion is not completely understood and several activities are thought to be involved in processing of 3'-PG ends. In this study we examined activities in human whole cell extracts (WCE) responsible for removal of 3'-PG. Using a radiolabelled oligonucleotide containing a single nucleotide gap with internal 5'-phosphate and 3'-PG ends, we demonstrate that the major 3'-PG activity in human WCE is Mg2+ dependent and that this activity co-purifies with AP endonuclease 1 (APE1) over phosphocellulose and gel filtration chromatography. Furthermore, immunodepletion of APE1 from active gel filtration fractions using APE1 specific antibodies reveals that the major activity against 3'-PG in human WCE is APE1.
Figures
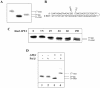

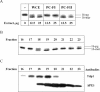

References
-
- Lindahl T. (1993) Instability and decay of the primary structure of DNA. Nature, 362, 709–715. - PubMed
-
- Dedon P.C. and Goldberg,I.H. (1992) Free-radical mechanisms involved in the formation of sequence-dependent bistranded DNA lesions by the antitumor antibiotics bleomycin, neocarzinostatin, and calicheamicin. Chem. Res. Toxicol., 5, 311–332. - PubMed
-
- Henle E.S. and Linn,S. (1997) Formation, prevention, and repair of DNA damage by iron/hydrogen peroxide. J. Biol. Chem., 272, 19095–19098. - PubMed
-
- Demple B. and DeMott,M.S. (2002) Dynamics and diversions in base excision DNA repair of oxidized abasic lesions. Oncogene, 21, 8926–8934. - PubMed
-
- Kane C.M. and Linn,S. (1981) Purification and characterization of an apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease from HeLa cells. J. Biol. Chem., 256, 3405–3414. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

