Helicase-dependent isothermal DNA amplification
- PMID: 15247927
- PMCID: PMC1249482
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.embor.7400200
Helicase-dependent isothermal DNA amplification
Abstract
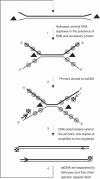
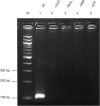
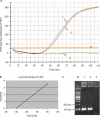
Polymerase chain reaction is the most widely used method for in vitro DNA amplification. However, it requires thermocycling to separate two DNA strands. In vivo, DNA is replicated by DNA polymerases with various accessory proteins, including a DNA helicase that acts to separate duplex DNA. We have devised a new in vitro isothermal DNA amplification method by mimicking this in vivo mechanism. Helicase-dependent amplification (HDA) utilizes a DNA helicase to generate single-stranded templates for primer hybridization and subsequent primer extension by a DNA polymerase. HDA does not require thermocycling. In addition, it offers several advantages over other isothermal DNA amplification methods by having a simple reaction scheme and being a true isothermal reaction that can be performed at one temperature for the entire process. These properties offer a great potential for the development of simple portable DNA diagnostic devices to be used in the field and at the point-of-care.
Figures


References
-
- Ali JA, Maluf NK, Lohman TM (1999) An oligomeric form of E. coli UvrD is required for optimal helicase activity. J Mol Biol 293: 815–834 - PubMed
-
- Andras SC, Power JB, Cocking EC, Davey MR (2001) Strategies for signal amplification in nucleic acid detection. Mol Biotechnol 19: 29–44 - PubMed
-
- Bujalowski W, Lohman TM (1989) Negative co-operativity in Escherichia coli single strand binding protein–oligonucleotide interactions. II. Salt, temperature and oligonucleotide length effects. J Mol Biol 207: 269–288 - PubMed
-
- Caruthers JM, McKay DB (2002) Helicase structure and mechanism. Curr Opin Struct Biol 12: 123–133 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
