Evidence for a novel late-onset Alzheimer disease locus on chromosome 19p13.2
- PMID: 15248153
- PMCID: PMC1182019
- DOI: 10.1086/423393
Evidence for a novel late-onset Alzheimer disease locus on chromosome 19p13.2
Abstract
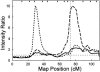
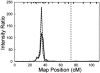
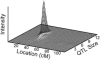
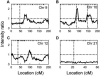
Late-onset familial Alzheimer disease (LOFAD) is a genetically heterogeneous and complex disease for which only one locus, APOE, has been definitively identified. Difficulties in identifying additional loci are likely to stem from inadequate linkage analysis methods. Nonparametric methods suffer from low power because of limited use of the data, and traditional parametric methods suffer from limitations in the complexity of the genetic model that can be feasibly used in analysis. Alternative methods that have recently been developed include Bayesian Markov chain-Monte Carlo methods. These methods allow multipoint linkage analysis under oligogenic trait models in pedigrees of arbitrary size; at the same time, they allow for inclusion of covariates in the analysis. We applied this approach to an analysis of LOFAD on five chromosomes with previous reports of linkage. We identified strong evidence of a second LOFAD gene on chromosome 19p13.2, which is distinct from APOE on 19q. We also obtained weak evidence of linkage to chromosome 10 at the same location as a previous report of linkage but found no evidence for linkage of LOFAD age-at-onset loci to chromosomes 9, 12, or 21.
Figures

References
Electronic-Database Information
-
- Marshfield Center for Medical Genetics, http://research.marshfieldclinic.org/genetics/ (for genetic maps)
-
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Omim/ (for APP, PSEN1, PSEN2, APOE, MAPT, PRP, A2M, LRP, LDLR, PIN1, ELAV1, and ELAV3)
References
-
- Bacanu SA, Devlin B, Chowdari KV, DeKosky ST, Nimgaonkar VL, Sweet RA (2002) Linkage analysis of Alzheimer disease with psychosis. Neurology 59:118–120 - PubMed
-
- Bennett C, Crawford F, Osborne A, Diaz P, Hoyne J, Lopez R, Roques P, Duara R, Rossor M, Mullan M (1995) Evidence that the APOE locus influences rate of disease progression in late-onset familial Alzheimer’s disease but is not causative. Am J Med Genet 60:1–6 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U24 AG021886/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM046255/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM 46255/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005136/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AG011762/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG008017/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG021544/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG 21544/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG 08017/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG011762/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R37 GM046255/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- AG 11762/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG 05136/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

