Renal clearance and daily excretion of cortisol and adrenal androgens in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus
- PMID: 15249323
- PMCID: PMC1755103
- DOI: 10.1136/ard.2003.014274
Renal clearance and daily excretion of cortisol and adrenal androgens in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus
Abstract
Background: In rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), patients demonstrate low levels of adrenal hormones.
Objective: To investigate whether increased renal clearance and daily excretion contribute to this phenomenon.
Methods: Thirty patients with RA, 32 with SLE, and 54 healthy subjects (HS) participated. Serum and urinary levels of cortisol, cortisone, 17-hydroxyprogesterone (17OHP), androstenedione, dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA), and DHEA sulphate (DHEAS) were measured.
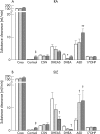
Results: Clearance of DHEAS and DHEA was lower in patients than in HS, and clearance of androstenedione was somewhat higher in patients than in HS, but daily excretion of this latter hormone was low. Clearance of cortisol, cortisone, and 17OHP was similar between the groups. The total molar amount per hour of excreted DHEA, DHEAS, and androstenedione was lower in patients than HS (but similar for cortisol). Serum DHEAS levels correlated with urinary DHEAS levels in HS and patients, whereby HS excreted 5-10 times more of this hormone than excreted by patients. Low serum levels of adrenal androgens and cortisol in patients as compared with HS were confirmed, and proteinuria was not associated with changes of measured renal parameters.
Conclusions: This study in patients with RA and SLE demonstrates that low serum levels of adrenal androgens and cortisol are not due to increased renal clearance and daily loss of these hormones. Decreased adrenal production or increased conversion or conjugation to downstream hormones are the most likely causes of inadequately low serum levels of adrenal hormones in RA and SLE.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Serum levels of pregnenolone and 17-hydroxypregnenolone in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus: relation to other adrenal hormones.J Rheumatol. 2003 Feb;30(2):269-75. J Rheumatol. 2003. PMID: 12563679
-
Possible role of leptin in hypoandrogenicity in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis.Ann Rheum Dis. 2004 Jul;63(7):809-16. doi: 10.1136/ard.2003.011619. Ann Rheum Dis. 2004. PMID: 15194576 Free PMC article.
-
Inadequately low serum levels of steroid hormones in relation to interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor in untreated patients with early rheumatoid arthritis and reactive arthritis.Arthritis Rheum. 2002 Mar;46(3):654-62. doi: 10.1002/art.10177. Arthritis Rheum. 2002. PMID: 11920401
-
Adrenal androgens and the immune system.Semin Reprod Med. 2004 Nov;22(4):369-77. doi: 10.1055/s-2004-861553. Semin Reprod Med. 2004. PMID: 15635504 Review.
-
Perturbations of hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis and adrenal androgen functions in rheumatoid arthritis: an odyssey of hormonal relationships to the disease.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1999 Jun 22;876:53-62; discussion 62-3. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1999.tb07622.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1999. PMID: 10415593 Review.
Cited by
-
Population-based case-control study revealed metabolomic biomarkers of suboptimal health status in Chinese population-potential utility for innovative approach by predictive, preventive, and personalized medicine.EPMA J. 2020 Mar 23;11(2):147-160. doi: 10.1007/s13167-020-00200-7. eCollection 2020 Jun. EPMA J. 2020. PMID: 32549914 Free PMC article.
-
Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal Hypofunction in Myalgic Encephalomyelitis (ME)/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (CFS) as a Consequence of Activated Immune-Inflammatory and Oxidative and Nitrosative Pathways.Mol Neurobiol. 2017 Nov;54(9):6806-6819. doi: 10.1007/s12035-016-0170-2. Epub 2016 Oct 20. Mol Neurobiol. 2017. PMID: 27766535 Review.
-
Cuproptosis and cuproptosis-related genes in rheumatoid arthritis: Implication, prospects, and perspectives.Front Immunol. 2022 Aug 4;13:930278. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.930278. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35990673 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Steroid hormones and influence of therapeutic drugs in Chinese postmenopausal rheumatoid arthritis patients.Front Immunol. 2025 May 12;16:1589798. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1589798. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40421020 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of Various Systemic and Organ-Specific Autoimmune Markers in Addison's Disease Patients Compared to Healthy Controls.J Clin Med. 2025 Jun 3;14(11):3951. doi: 10.3390/jcm14113951. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40507712 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

