Standard reference values for musculoskeletal ultrasonography
- PMID: 15249327
- PMCID: PMC1755091
- DOI: 10.1136/ard.2003.015081
Standard reference values for musculoskeletal ultrasonography
Abstract
Objectives: To determine standard reference values for musculoskeletal ultrasonography in healthy adults.
Methods: Ultrasonography was performed on 204 shoulders, elbows, hands, hips, knees, and feet of 102 healthy volunteers (mean age 38.4 years; range 20-60; 54 women) with a linear probe (10-5 MHz; Esaote Technos MP). Diameters of tendons, bursae, cartilage, erosions, hypoechoic rims around tendons and at joints were measured with regard to established standard scans. Mean, minimum, and maximum values, as well as two standard deviations (2 SD) were determined. Mean values +/-2 SD were defined as standard reference values.
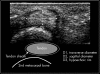
Results: Hypoechoic rims were normally present in joints and tendon sheaths owing to physiological synovial fluid and/or cartilage. Similarly, fluid was found in the subdeltoid bursa in 173/204 (85%), at the long biceps tendon in 56 (27%), in the suprapatellar recess in 158 (77%), in the popliteal bursae in 32 (16%), and in the retrocalcaneal bursa in 49 (24%). Erosions of >1 mm were seen at the humeral head in 47 (23%). Values for important intervals were determined. The correlation between two investigators was 0.96 (0.78-0.99). The reliability of follow up investigations was 0.83 (0.52-0.99).
Conclusions: Fluid in bursae as well as hypoechoic rims within joints and around tendons are common findings in healthy people. This study defines standard reference values for musculoskeletal ultrasonography to prevent misinterpretation of normal fluid as an anatomical abnormality.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Standardized, musculoskeletal ultrasonographic reference values for healthy Korean adults.Korean J Intern Med. 2019 Nov;34(6):1372-1380. doi: 10.3904/kjim.2016.397. Epub 2018 May 4. Korean J Intern Med. 2019. PMID: 29722248 Free PMC article.
-
Sonographic appearance of fluid in peripheral joints and bursae of healthy asymptomatic Chinese population.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2018 Sep;8(8):781-787. doi: 10.21037/qims.2018.09.10. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2018. PMID: 30306058 Free PMC article.
-
Synovial fluid in the hindfoot and ankle: detection of amount and distribution with US.Radiology. 1995 Oct;197(1):275-8. doi: 10.1148/radiology.197.1.7568837. Radiology. 1995. PMID: 7568837
-
Overview of musculoskeletal sonography.Ultrasound Q. 2010 Mar;26(1):27-35. doi: 10.1097/RUQ.0b013e3181ce43ed. Ultrasound Q. 2010. PMID: 20216192 Review.
-
Applications of musculoskeletal sonography.J Clin Ultrasound. 1999 Jul-Aug;27(6):293-318. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1097-0096(199907/08)27:6<293::aid-jcu1>3.0.co;2-c. J Clin Ultrasound. 1999. PMID: 10395126 Review.
Cited by
-
Pediatric musculoskeletal ultrasound: age- and sex-related normal B-mode findings of the knee.Rheumatol Int. 2016 Nov;36(11):1569-1577. doi: 10.1007/s00296-016-3528-x. Epub 2016 Jul 11. Rheumatol Int. 2016. PMID: 27401002
-
Ultrasound imaging in rheumatoid arthritis.Radiol Med. 2019 Nov;124(11):1087-1100. doi: 10.1007/s11547-019-01002-2. Epub 2019 Mar 9. Radiol Med. 2019. PMID: 30852792 Review.
-
Ultrasonography in the assessment of peripheral joint involvement in psoriatic arthritis : a comparison with radiography, MRI and scintigraphy.Clin Rheumatol. 2008 Aug;27(8):983-9. doi: 10.1007/s10067-008-0835-y. Epub 2008 Feb 8. Clin Rheumatol. 2008. PMID: 18259687
-
Diagnostic Ultrasound Shows Preferential Activation of Rectus Abdominis Segments with Exercises Targeting Upper Versus Lower Segments.Int J Exerc Sci. 2023 Aug 1;16(1):1077-1086. doi: 10.70252/BZWN2771. eCollection 2023. Int J Exerc Sci. 2023. PMID: 38288259 Free PMC article.
-
Utility of ultrasound joint counts in the prediction of rheumatoid arthritis in patients with very early synovitis.Ann Rheum Dis. 2011 Mar;70(3):500-7. doi: 10.1136/ard.2010.131573. Epub 2010 Nov 29. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011. PMID: 21115552 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

