Contribution of the p38MAPK signalling pathway to proliferation in human cultured airway smooth muscle cells is mitogen-specific
- PMID: 15249425
- PMCID: PMC1575175
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705809
Contribution of the p38MAPK signalling pathway to proliferation in human cultured airway smooth muscle cells is mitogen-specific
Abstract
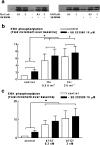
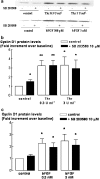
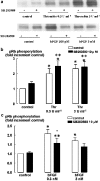
We have investigated the role of p38MAPK in human airway smooth muscle (HASM) proliferation in response to thrombin and bFGF. The regulation of cyclin D1 mRNA, cyclin D1, cyclin E and p21Cip1 protein levels, and the extent of retinoblastoma protein (pRb) phosphorylation in response to activation of p38MAPK have also been examined. Two distinct inhibitors of p38MAPK, SB 203580 (10 microm) and SB 202190 (10 microm), prevented bFGF (0.3-3 nm)-stimulated cell proliferation, but had no effect on the response to thrombin (0.3-3 U ml(-1)). In cells incubated with thrombin or bFGF for 20 h, there was an increase in p38MAPK phosphorylation in response to bFGF, but not to thrombin. Thrombin and bFGF-stimulated increases in ERK phosphorylation and cyclin D1 mRNA and protein levels were not influenced by SB 203580 pre-treatment. Similarly, cyclin E and p21Cip1 protein levels, measured after 20 h incubation with mitogen, did not appear to be regulated by SB 203580 (10 microm). Although both thrombin and bFGF significantly increased levels of pRb phosphorylation, SB 203580 (10 microm) inhibited only bFGF-stimulated pRb phosphorylation. In addition, SB 203580 (10 microm) selectively inhibited bFGF-stimulated DNA synthesis, suggesting that the antimitogenic actions of SB 203580 on pRb phosphorylation cause cell cycle arrest at late G1 phase. In conclusion, these results indicate that p38MAPK is involved in bFGF-, but not in thrombin-stimulated HASM proliferation. The activation of the p38MAPK pathway by bFGF, but not by thrombin, regulates the phosphorylation of pRb without influencing cyclin D1 expression.
Copyright 2004 Nature Publishing Group
Figures

Similar articles
-
The importance of ERK activity in the regulation of cyclin D1 levels and DNA synthesis in human cultured airway smooth muscle.Br J Pharmacol. 2000 Sep;131(1):17-28. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0703454. Br J Pharmacol. 2000. PMID: 10960064 Free PMC article.
-
Glucocorticoids inhibit proliferation, cyclin D1 expression, and retinoblastoma protein phosphorylation, but not activity of the extracellular-regulated kinases in human cultured airway smooth muscle.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1999 Jul;21(1):77-88. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb.21.1.3396. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1999. PMID: 10385595
-
Beta2-adrenergic receptor agonists and cAMP arrest human cultured airway smooth muscle cells in the G(1) phase of the cell cycle: role of proteasome degradation of cyclin D1.Mol Pharmacol. 1999 Nov;56(5):1079-86. doi: 10.1124/mol.56.5.1079. Mol Pharmacol. 1999. PMID: 10531416
-
The potential and limitations of p38MAPK as a drug target for the treatment of hematological malignancies.Curr Drug Targets. 2010 Jul;11(7):823-33. doi: 10.2174/138945010791320854. Curr Drug Targets. 2010. PMID: 20370645 Review.
-
Signal transduction mediated by cyclin D1: from mitogens to cell proliferation: a molecular target with therapeutic potential.Cancer Treat Res. 2004;119:217-37. doi: 10.1007/1-4020-7847-1_11. Cancer Treat Res. 2004. PMID: 15164880 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Transferrin-receptor-mediated iron accumulation controls proliferation and glutamate release in glioma cells.J Mol Med (Berl). 2009 Feb;87(2):153-67. doi: 10.1007/s00109-008-0414-3. Epub 2008 Dec 9. J Mol Med (Berl). 2009. PMID: 19066835
-
Functional expression of IgG-Fc receptors in human airway smooth muscle cells.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2011 May;44(5):665-72. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2009-0371OC. Epub 2010 Jul 1. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 20595464 Free PMC article.
-
Key Role of ROS in the Process of 15-Lipoxygenase/15-Hydroxyeicosatetraenoiccid-Induced Pulmonary Vascular Remodeling in Hypoxia Pulmonary Hypertension.PLoS One. 2016 Feb 12;11(2):e0149164. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0149164. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26871724 Free PMC article.
-
Crosstalk Between Signaling Pathways Involved in the Regulation of Airway Smooth Muscle Cell Hyperplasia.Front Pharmacol. 2019 Oct 9;10:1148. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.01148. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31649532 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Airway epithelium stimulates smooth muscle proliferation.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2009 Sep;41(3):297-304. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2008-0358OC. Epub 2009 Jan 16. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 19151317 Free PMC article.
References
-
- ADAM R.M., ROTH J.A., CHENG H.L., RICE D.C., KHOURY J., BAUER S.B., PETERS C.A., FREEMAN M.R. Signaling through PI3K/Akt mediates stretch and PDGF-BB-dependent DNA synthesis in bladder smooth muscle cells. J. Urol. 2003;169:2388–2393. - PubMed
-
- AWAD M.M., ENSLEN H., BOYLAN J.M., DAVIS R.J., GRUPPUSO P.A. Growth regulation via p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase in developing liver. J. Biol. Chem. 2000a;275:38716–38721. - PubMed
-
- AWAD M.M., GRUPPUSO P.A. Cell cycle control during liver development in the rat: evidence indicating a role for cyclin D1 posttranscriptional regulation. Cell Growth Differ. 2000b;11:325–334. - PubMed
-
- BARON W., METZ B., BANSAL R., HOEKSTRA D., DE VRIES H. PDGF and FGF-2 signaling in oligodendrocyte progenitor cells: regulation of proliferation and differentiation by multiple intracellular signaling pathways. Mol. Cell Neurosci. 2000;15:314–329. - PubMed
-
- CASANOVAS O., MIRO F., ESTANYOL J.M., ITARTE E., AGELL N., BACHS O. Osmotic stress regulates the stability of cyclin D1 in a p38SAPK2-dependent manner. J. Biol. Chem. 2000;275:35091–35097. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

