Lack of Toll-like receptor 4 or myeloid differentiation factor 88 reduces atherosclerosis and alters plaque phenotype in mice deficient in apolipoprotein E
- PMID: 15249654
- PMCID: PMC489994
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0403249101
Lack of Toll-like receptor 4 or myeloid differentiation factor 88 reduces atherosclerosis and alters plaque phenotype in mice deficient in apolipoprotein E
Abstract
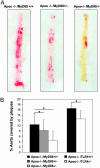
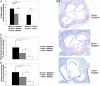
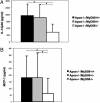
Toll-like receptors (TLRs) and the downstream adaptor molecule myeloid differentiation factor 88 (MyD88) play an essential role in the innate immune responses. Here, we demonstrate that genetic deficiency of TLR4 or MyD88 is associated with a significant reduction of aortic plaque areas in atherosclerosis-prone apolipoprotein E-deficient mice, despite persistent hypercholesterolemia, implying an important role for the innate immune system in atherogenesis. Apolipoprotein E-deficient mice that also lacked TLR4 or MyD88 demonstrated reduced aortic atherosclerosis that was associated with reductions in circulating levels of proinflammatory cytokines IL-12 or monocyte chemoattractant protein 1, plaque lipid content, numbers of macrophage, and cyclooxygenase 2 immunoreactivity in their plaques. Endothelial-leukocyte adhesion in response to minimally modified low-density lipoprotein was reduced in aortic endothelial cells derived from MyD88-deficient mice. Taken together, our results suggest an important role for TLR4 and MyD88 signaling in atherosclerosis in a hypercholesterolemic mouse model, providing a pathophysiologic link between innate immunity, inflammation, and atherogenesis.
Figures
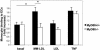
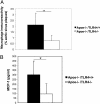
References
-
- Ross, R. (1999) N. Engl. J. Med. 340, 115–126. - PubMed
-
- Glass, C. K. & Witztum, J. L. (2001) Cell 104, 503–516. - PubMed
-
- Shah, P. K. (2003) J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 41, 15S–22S. - PubMed
-
- Libby, P. (2002) Nature 420, 868–874. - PubMed
-
- Hansson, G. K., Libby, P., Schonbeck, U. & Yan, Z. Q. (2002) Circ. Res. 91, 281–291. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

