Retrovirus resistance factors Ref1 and Lv1 are species-specific variants of TRIM5alpha
- PMID: 15249685
- PMCID: PMC490010
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0402361101
Retrovirus resistance factors Ref1 and Lv1 are species-specific variants of TRIM5alpha
Abstract
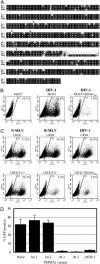
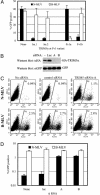
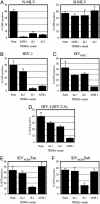
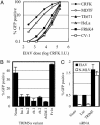
Mammalian cells express several factors that act in a cell-autonomous manner to inhibit retrovirus replication. Among these are the Friend virus susceptibility factor 1/lentivirus susceptibility factor 1/restriction factor 1 (Ref1) class of restriction factors, which block infection by targeting the capsids of diverse retroviruses. Here we show that lentivirus susceptibility factor 1 and Ref1 are species-specific variants of tripartite interaction motif 5alpha (TRIM5alpha), a cytoplasmic body component recently shown to block HIV-1 infection in rhesus macaque cells, and can indeed block infection by widely divergent retroviruses. Depletion of TRIM5alpha from human cells relieved restriction of N-tropic murine leukemia virus (N-MLV), and expression of human TRIM5alpha in otherwise nonrestricting cells conferred specific resistance to N-MLV infection, indicating that TRIM5alpha is Ref1 or an essential component of Ref1. TRIM5alpha variants from humans, rhesus monkeys, and African green monkeys displayed different but overlapping restriction specificities that were quite accurately predicted by the restriction properties of the cells from which they were derived. All TRIM5alpha variants could inhibit infection by at least two different retroviruses, and African green monkey TRIM5alpha was able to inhibit infection by no less than four divergent retroviruses of human, non-human primate, equine, and murine origin. However, each TRIM5alpha variant was unable to restrict retroviruses isolated from the same species. These data indicate that TRIM5alpha can confer broad innate immunity to retrovirus infection in primate cells and is likely to be an important natural barrier to cross-species retrovirus transmission.
Figures
Comment in
-
In defense of the cell: TRIM5alpha interception of mammalian retroviruses.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Jul 20;101(29):10496-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0404066101. Epub 2004 Jul 13. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004. PMID: 15252204 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Sheehy, A. M., Gaddis, N. C., Choi, J. D. & Malim, M. H. (2002) Nature 418, 646-650. - PubMed
-
- Harris, R. S., Bishop, K. N., Sheehy, A. M., Craig, H. M., Petersen-Mahrt, S. K., Watt, I. N., Neuberger, M. S. & Malim, M. H. (2003) Cell 113, 803-809. - PubMed
-
- Mangeat, B., Turelli, P., Caron, G., Friedli, M., Perrin, L. & Trono, D. (2003) Nature 424, 99-103. - PubMed
-
- Gao, G., Guo, X. & Goff, S. P. (2002) Science 297, 1703-1706. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

