Evaluating heterogeneity in cumulative meta-analyses
- PMID: 15251035
- PMCID: PMC487901
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2288-4-18
Evaluating heterogeneity in cumulative meta-analyses
Abstract
Background: Recently developed measures such as I2 and H allow the evaluation of the impact of heterogeneity in conventional meta-analyses. There has been no examination of the development of heterogeneity in the context of a cumulative meta-analysis.
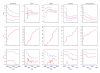
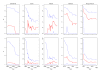
Methods: Cumulative meta-analyses of five smoking cessation interventions (clonidine, nicotine replacement therapy using gum and patch, physician advice and acupuncture) were used to calculate I2 and H. These values were plotted by year of publication, control event rate and sample size to trace the development of heterogeneity over these covariates.
Results: The cumulative evaluation of heterogeneity varied according to the measure of heterogeneity used and the basis of cumulation. Plots produced from the calculations revealed areas of heterogeneity useful in the consideration of potential sources for further study.
Conclusion: The examination of heterogeneity in conjunction with summary effect estimates in a cumulative meta-analysis offered valuable insight into the evolution of variation. Such information is not available in the context of conventional meta-analysis and has the potential to lead to the development of a richer picture of the effectiveness of interventions.
Figures

References
-
- Mulrow CD. The medical review article: state of the science. Ann Intern Med. 1987;106:485–488. - PubMed
-
- Mulrow CD, Thacker SB, Pugh JA. A proposal for more informative abstracts of review articles. Ann Intern Med. 1988;108:613–615. - PubMed
-
- Lau J, Antman EM, Jimenez-Silva J, Kupelnick B, Mosteller F, Chalmers TC. Cumulative meta-analysis of therapeutic trials for myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med. 1992;327:248–254. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

