A requirement for Notch1 distinguishes 2 phases of definitive hematopoiesis during development
- PMID: 15251982
- PMCID: PMC5998659
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2004-03-1224
A requirement for Notch1 distinguishes 2 phases of definitive hematopoiesis during development
Abstract
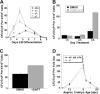
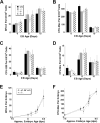
Notch1 is known to play a critical role in regulating fates in numerous cell types, including those of the hematopoietic lineage. Multiple defects exhibited by Notch1-deficient embryos confound the determination of Notch1 function in early hematopoietic development in vivo. To overcome this limitation, we examined the developmental potential of Notch1(-/-) embryonic stem (ES) cells by in vitro differentiation and by in vivo chimera analysis. Notch1 was found to affect primitive erythropoiesis differentially during ES cell differentiation and in vivo, and this result reflected an important difference in the regulation of Notch1 expression during ES cell differentiation relative to the developing mouse embryo. Notch1 was dispensable for the onset of definitive hematopoiesis both in vitro and in vivo in that Notch1(-/-) definitive progenitors could be detected in differentiating ES cells as well as in the yolk sac and early fetal liver of chimeric mice. Despite the fact that Notch1(-/-) cells can give rise to multiple types of definitive progenitors in early development, Notch1(-/-) cells failed to contribute to long-term definitive hematopoiesis past the early fetal liver stage in the context of a wild-type environment in chimeric mice. Thus, Notch1 is required, in a cell-autonomous manner, for the establishment of long-term, definitive hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs).
Figures
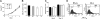
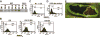

References
-
- Palis J, Robertson S, Kennedy M, Wall C, Keller G. Development of erythroid and myeloid progenitors in the yolk sac and embryo proper of the mouse. Development. 1999;126:5073–5084. - PubMed
-
- McGrath KE, Koniski AD, Malik J, Palis J. Circulation is established in a stepwise pattern in the mammalian embryo. Blood. 2003;101:1669–1676. - PubMed
-
- Godin IE, Garcia-Porrero JA, Coutinho A, Dieterlen-Lievre F, Marcos MA. Para-aortic splanchnopleura from early mouse embryos contains B1a cell progenitors. Nature. 1993;364:67–70. - PubMed
-
- Cumano A, Dieterlen-Lievre F, Godin I. Lymphoid potential, probed before circulation in mouse, is restricted to caudal intraembryonic splanchnopleura. Cell. 1996;86:907–916. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

