Conservative homologous recombination preferentially repairs DNA double-strand breaks in the S phase of the cell cycle in human cells
- PMID: 15252152
- PMCID: PMC484186
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkh703
Conservative homologous recombination preferentially repairs DNA double-strand breaks in the S phase of the cell cycle in human cells
Abstract
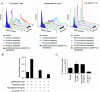
DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) are repaired by either homologous recombination (HR) or non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) in mammalian cells. Repair with NHEJ or HR using single-strand annealing (SSA) often results in deletions and is generally referred to as non-conservative recombination. Error-free, conservative HR involves strand invasion and requires a homologous DNA template, and therefore it is generally believed that this type of repair occurs preferentially in the late S, G2 and M phases of the cell cycle, when the sister chromatid is available. There are several observations supporting this hypothesis, although it has not been tested directly. Here, we synchronize human SW480SN.3 cells in the G1/G0 (with serum starvation), S (with thymidine block) and M (with nocodazole) phases of the cell cycle and investigate the efficiency of conservative HR repair of an I-SceI-induced DSB. The frequency of HR repair of DSBs was 39 times higher in S-phase cells than in M-phase cells and 24-fold higher than in G1/G0 cells. This low level of conservative HR occurs even though a homologous template is present within the recombination substrate. We propose that this can be explained by an absence of recombination proteins outside the S phase or alternatively that there maybe factors that suppress HR in G1/G0 and M. Furthermore, we found that HR repair of DSBs involves short tract gene conversion in all the phases of the cell cycle. This indicates that the same pathway for conservative HR is employed in the repair of DSBs regardless of phase of the cell cycle and that only the frequency is affected.
Figures

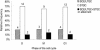
References
-
- van Gent D.C., Hoeijmakers,J.H. and Kanaar,R. (2001) Chromosomal stability and the DNA double-stranded break connection. Nature Rev. Genet., 2, 196–206. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

