Radionuclide techniques for the assessment of myocardial viability and hibernation
- PMID: 15254006
- PMCID: PMC1876321
- DOI: 10.1136/hrt.2002.007575
Radionuclide techniques for the assessment of myocardial viability and hibernation
Figures
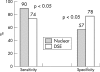
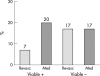
Similar articles
-
Radionuclide techniques for myocardial viability and hibernation.Heart. 1999 Jan;81(1):6-7. doi: 10.1136/hrt.81.1.6. Heart. 1999. PMID: 10220535 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
New applications of myocardial perfusion imaging.Tex Heart Inst J. 1996;23(2):122-7. Tex Heart Inst J. 1996. PMID: 8792543 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Myocardial viability: contractile reserve or cell membrane integrity?J Am Coll Cardiol. 1996 Aug;28(2):443-6. doi: 10.1016/0735-1097(96)83110-X. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1996. PMID: 8800123 No abstract available.
-
Role of cardiac magnetic resonance imaging in the assessment of myocardial viability.Circulation. 2004 Mar 23;109(11):1328-34. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000120294.67948.E3. Circulation. 2004. PMID: 15037539 Review. No abstract available.
-
Disparity in coronary perfusion and regional wall motion: effect on clinical assessment of viability.Coron Artery Dis. 1993 Jun;4(6):512-20. doi: 10.1097/00019501-199306000-00005. Coron Artery Dis. 1993. PMID: 8261229 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Non-invasive cardiac imaging technologies for the assessment of myocardial viability: a summary of evidence-based analyses.Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2010;10(14):1-24. Epub 2010 Jul 1. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2010. PMID: 23074391 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Assessment of left ventricular function: visual or quantitative?Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2011 Apr;27(4):573-7. doi: 10.1007/s10554-010-9735-8. Epub 2010 Oct 28. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2011. PMID: 20981573 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
The use of nuclear imaging to assess the myocardial viability.J Saudi Heart Assoc. 2010 Jul;22(3):157-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jsha.2010.04.004. Epub 2010 Jul 14. J Saudi Heart Assoc. 2010. PMID: 23960613 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Positron emission tomography; viable tool in patients pre-CABG?Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2010 Aug;26(6):661-4. doi: 10.1007/s10554-010-9612-5. Epub 2010 Apr 1. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2010. PMID: 20358291 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Direct imaging of viable myocardium by gated SPECT in patients with ischaemic left ventricular dysfunction.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2010 Aug;37(9):1730-5. doi: 10.1007/s00259-010-1463-8. Epub 2010 Apr 24. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2010. PMID: 20419371
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
