Coexistence of gamma and high-frequency oscillations in rat medial entorhinal cortex in vitro
- PMID: 15254156
- PMCID: PMC1665136
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2004.068973
Coexistence of gamma and high-frequency oscillations in rat medial entorhinal cortex in vitro
Abstract
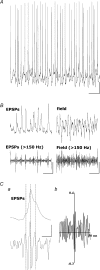
High frequency oscillations (> 80-90 Hz) occur in neocortex and hippocampus in vivo where they are associated with specific behavioural states and more classical EEG frequency bands. In the hippocampus in vitro these oscillations can occur in the absence of pyramidal neuronal somatodendritic compartments and are temporally correlated with on-going, persistent gamma frequency oscillations. Their occurrence in the hippocampus is dependent on gap-junctional communication and it has been suggested that these high frequency oscillations originate as collective behaviour in populations of electrically coupled principal cell axonal compartments. Here we demonstrate that the superficial layers of medial entorhinal cortex can also generate high frequency oscillations associated with gamma rhythms. During persistent gamma frequency oscillations high frequency oscillations occur with a high bispectral coherence with the field gamma activity. Bursts of high frequency oscillations are temporally correlated with both the onset of compound excitatory postsynaptic potentials in fast-spiking interneurones and spikelet potentials in both pyramidal and stellate principal neurones. Both the gamma frequency and high frequency oscillations were attenuated by the gap junction blocker carbenoxolone. These data suggest that high frequency oscillations may represent the substrate for phasic drive to interneurones during persistent gamma oscillations in the medial entorhinal cortex.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Gamma oscillations induced by kainate receptor activation in the entorhinal cortex in vitro.J Neurosci. 2003 Oct 29;23(30):9761-9. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-30-09761.2003. J Neurosci. 2003. PMID: 14586003 Free PMC article.
-
Ripple activity in the dentate gyrus of dishinibited hippocampus-entorhinal cortex slices.J Neurosci Res. 2005 Apr 1;80(1):92-103. doi: 10.1002/jnr.20440. J Neurosci Res. 2005. PMID: 15742360
-
High-frequency oscillations in human brain.Hippocampus. 1999;9(2):137-42. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1098-1063(1999)9:2<137::AID-HIPO5>3.0.CO;2-0. Hippocampus. 1999. PMID: 10226774
-
Persistent gamma oscillations in superficial layers of rat auditory neocortex: experiment and model.J Physiol. 2005 Jan 1;562(Pt 1):3-8. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2004.074641. Epub 2004 Oct 15. J Physiol. 2005. PMID: 15489250 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interneuron diversity series: inhibitory interneurons and network oscillations in vitro.Trends Neurosci. 2003 Dec;26(12):676-82. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2003.09.016. Trends Neurosci. 2003. PMID: 14624852 Review.
Cited by
-
Background synaptic activity in rat entorhinal cortex shows a progressively greater dominance of inhibition over excitation from deep to superficial layers.PLoS One. 2014 Jan 15;9(1):e85125. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0085125. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24454801 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of network oscillatory activity and GABAergic synaptic transmission by CB1 cannabinoid receptors in the rat medial entorhinal cortex.Neural Plast. 2008;2008:808564. doi: 10.1155/2008/808564. Epub 2008 Dec 1. Neural Plast. 2008. PMID: 19079598 Free PMC article.
-
Virtual Electrode Recording Tool for EXtracellular potentials (VERTEX): comparing multi-electrode recordings from simulated and biological mammalian cortical tissue.Brain Struct Funct. 2015 Jul;220(4):2333-53. doi: 10.1007/s00429-014-0793-x. Epub 2014 May 27. Brain Struct Funct. 2015. PMID: 24863422 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of contralateral noise on the 20-Hz auditory steady state response--magnetoencephalography study.PLoS One. 2014 Jun 10;9(6):e99457. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0099457. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24915061 Free PMC article.
-
Decreased BOLD signals elicited by 40-Hz auditory stimulation of the right primary auditory cortex in bipolar disorder: An fMRI study.Front Psychiatry. 2022 Sep 15;13:833896. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2022.833896. eCollection 2022. Front Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 36186861 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bragin A, Engel J, Jr, Wilson CL, Fried I, Mathern GW. Hippocampal and entorhinal cortex high-frequency oscillations (100–500 Hz) in human epileptic brain and in kainic acid – treated rats with chronic seizures. Epilepsia. 1999;40:127–137. - PubMed
-
- Brillinger DR. An introduction to polyspectra. Ann Math Statist. 1965;36:1351–1374.
-
- Brillinger DR, Rosenblatt M. Computation and interpretation of Kth-order spectra. In: Harris B, editor. Spectral Analysis of Time Series. New York: John Wiley; 1967. pp. 189–232.
-
- Buzsáki G, Horvath Z, Urioste R, Hetke J, Wise K. High-frequency network oscillation in the hippocampus. Science. 1992;256:1025–1027. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

