APOBEC3G targets specific virus species
- PMID: 15254195
- PMCID: PMC446120
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.78.15.8238-8244.2004
APOBEC3G targets specific virus species
Abstract
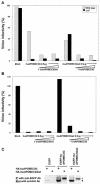
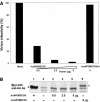
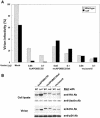
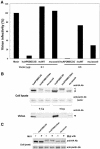
Human APOBEC3G (huAPOBEC3G), also known as CEM15, is a broad antiretroviral host factor that deaminates dC to dU in the minus strand DNA of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1), other lentiviruses, and murine leukemia virus (MLV), thereby creating G-to-A hypermutation in the plus strand DNA to inhibit the infectivity of these viruses. In this study, we examined the antiretroviral function of a murine homologue of APOBEC3G (muAPOBEC3G) on several retrovirus systems with different producer cells. MuAPOBEC3G did not suppress the infectivity of murine retroviral vectors produced from human or murine cells, whereas it showed antiviral activity on both wild-type and Deltavif virions of HIV-1 in human cells. In contrast, huAPOBEC3G showed broad antiviral activity on HIV-1 and murine retroviral vectors produced from human cells as well as murine cells. These data suggested that muAPOBEC3G does not possess antiretroviral activity on murine retroviruses and has a different target specificity from that of huAPOBEC3G and that huAPOBEC3G works as a broad antiviral factor not only in human cells but also in murine cells. A functional interaction study between human and murine APOBEC3G supported the former hypothesis. Furthermore, studies on the expression of APOBEC3G in producer cells and its incorporation into virions revealed that muAPOBEC3G is incorporated into HIV-1 virions but not into MLV virions. Thus, muAPOBEC3G cannot suppress the infectivity of murine retrovirus because it is not incorporated into virions. We suggest that murine retroviruses can replicate in murine target cells expressing muAPOBEC3G because they are not targets for this enzyme.
Figures


Similar articles
-
APOBEC3G targets human T-cell leukemia virus type 1.Retrovirology. 2005 May 19;2:32. doi: 10.1186/1742-4690-2-32. Retrovirology. 2005. PMID: 15943885 Free PMC article.
-
A single amino acid substitution in human APOBEC3G antiretroviral enzyme confers resistance to HIV-1 virion infectivity factor-induced depletion.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Apr 13;101(15):5652-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0400830101. Epub 2004 Mar 30. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004. PMID: 15054139 Free PMC article.
-
Antiviral function of APOBEC3G can be dissociated from cytidine deaminase activity.Curr Biol. 2005 Jan 26;15(2):166-70. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2004.12.068. Curr Biol. 2005. PMID: 15668174
-
Protecting APOBEC3G: a potential new target for HIV drug discovery.Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2005 Feb;6(2):141-7. Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2005. PMID: 15751736 Review.
-
Cytidine deaminases as a weapon against retroviruses and a new target for antiviral therapy.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2008 Mar;8(3):231-8. doi: 10.2174/138955708783744047. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2008. PMID: 18336343 Review.
Cited by
-
Retroelements versus APOBEC3 family members: No great escape from the magnificent seven.Front Microbiol. 2012 Aug 14;3:275. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2012.00275. eCollection 2012. Front Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22912627 Free PMC article.
-
Intracellular immunity to HIV-1: newly defined retroviral battles inside infected cells.Retrovirology. 2005 Apr 13;2:25. doi: 10.1186/1742-4690-2-25. Retrovirology. 2005. PMID: 15829012 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of APOBEC3DE as another antiretroviral factor from the human APOBEC family.J Virol. 2006 Nov;80(21):10522-33. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01123-06. Epub 2006 Aug 18. J Virol. 2006. PMID: 16920826 Free PMC article.
-
Species-specific inhibition of APOBEC3C by the prototype foamy virus protein bet.J Biol Chem. 2009 Feb 27;284(9):5819-26. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M808853200. Epub 2008 Dec 12. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19074429 Free PMC article.
-
Restriction of porcine endogenous retrovirus by porcine APOBEC3 cytidine deaminases.J Virol. 2011 Apr;85(8):3842-57. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01880-10. Epub 2011 Feb 9. J Virol. 2011. PMID: 21307203 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anant, S., A. J. MacGinnitie, and N. O. Davidson. 1995. apobec-1, the catalytic subunit of the mammalian apolipoprotein B mRNA editing enzyme, is a novel RNA-binding protein. J. Biol. Chem. 270:14762-14767. - PubMed
-
- Blanc, V., and N. O. Davidson. 2003. C-to-U RNA editing: mechanisms leading to genetic diversity. J. Biol. Chem. 278:1395-1398. - PubMed
-
- Burns, J. C., T. Friedmann, W. Driever, M. Burrascano, and J. K. Yee. 1993. Vesicular stomatitis virus G glycoprotein pseudotyped retroviral vectors: concentration to very high titer and efficient gene transfer into mammalian and nonmammalian cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90:8033-8037. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

